Nuclear power


Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear decay processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as Voyager 2.[1] Reactors producing controlled fusion power have been operated since 1958, but have yet to generate net power and are not expected to be commercially available in the near future.[2]
Most nuclear power plants use thermal reactors with enriched uranium in a once-through fuel cycle. Fuel is removed when the percentage of neutron absorbing atoms becomes so large that a chain reaction can no longer be sustained, typically three years. It is then cooled for several years in on-site spent fuel pools before being transferred to long-term storage. The spent fuel, though low in volume, is high-level radioactive waste. While its radioactivity decreases exponentially, it must be isolated from the biosphere for hundreds of thousands of years, though newer technologies (like fast reactors) have the potential to significantly reduce this. Because the spent fuel is still mostly fissionable material, some countries (e.g. France and Russia) reprocess their spent fuel by extracting fissile and fertile elements for fabrication into new fuel, although this process is more expensive than producing new fuel from mined uranium.[citation needed] All reactors breed some plutonium-239, which is found in the spent fuel, and because Pu-239 is the preferred material for nuclear weapons, reprocessing is seen as a weapon proliferation risk.
The first nuclear power plant was built in the 1950s. The global installed nuclear capacity grew to 100 GW in the late 1970s, and then expanded during the 1980s, reaching 300 GW by 1990. The 1979 Three Mile Island accident in the United States and the 1986 Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union resulted in increased regulation and public opposition to nuclear power plants. These factors, along with high cost of construction, resulted in the global installed capacity only increasing to 392 GW by 2023. These plants supplied 2,602 terawatt hours (TWh) of electricity in 2023, equivalent to about 9% of global electricity generation,[3] and were the second-largest low-carbon power source after hydroelectricity. As of November 2024,[update] there are 415 civilian fission reactors in the world, with overall capacity of 374 GW,[4] 66 under construction and 87 planned, with a combined capacity of 72 GW and 84 GW, respectively.[5] The United States has the largest fleet of nuclear reactors, generating almost 800 TWh of low-carbon electricity per year with an average capacity factor of 92%. The average global capacity factor is 89%.[4] Most new reactors under construction are generation III reactors in Asia.
Proponents contend that nuclear power is a safe, sustainable energy source that reduces carbon emissions. This is because nuclear power generation causes one of the lowest levels of fatalities per unit of energy generated compared to other energy sources. Coal, petroleum, natural gas and hydroelectricity have each caused more fatalities per unit of energy due to air pollution and accidents. Nuclear power plants also emit no greenhouse gases and result in less life-cycle carbon emissions than common "renewables". The radiological hazards associated with nuclear power are the primary motivations of the anti-nuclear movement, which contends that nuclear power poses many threats to people and the environment, citing the potential for accidents like the Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan in 2011, and is too expensive/slow to deploy when compared to alternative sustainable energy sources.
History
Origins

Nuclear fission was discovered in 1938 after over four decades of work on the science of radioactivity and the elaboration of new nuclear physics that described the components of atoms. Soon after the discovery of the fission process, it was realized that a fissioning nucleus can induce further nucleus fissions, thus inducing a self-sustaining chain reaction.[7] Once this was experimentally confirmed in 1939, scientists in many countries petitioned their governments for support for nuclear fission research, just on the cusp of World War II, in order to develop a nuclear weapon.[8]
In the United States, these research efforts led to the creation of the first man-made nuclear reactor, the Chicago Pile-1 under the Stagg Field stadium at the University of Chicago, which achieved criticality on December 2, 1942. The reactor's development was part of the Manhattan Project, the Allied effort to create atomic bombs during World War II. It led to the building of larger single-purpose production reactors for the production of weapons-grade plutonium for use in the first nuclear weapons. The United States tested the first nuclear weapon in July 1945, the Trinity test, and the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki happened one month later.


Despite the military nature of the first nuclear devices, there was strong optimism in the 1940s and 1950s that nuclear power could provide cheap and endless energy.[10] Electricity was generated for the first time by a nuclear reactor on December 20, 1951, at the EBR-I experimental station near Arco, Idaho, which initially produced about 100 kW.[11][12] In 1953, American President Dwight Eisenhower gave his "Atoms for Peace" speech at the United Nations, emphasizing the need to develop "peaceful" uses of nuclear power quickly. This was followed by the Atomic Energy Act of 1954 which allowed rapid declassification of U.S. reactor technology and encouraged development by the private sector.
First power generation
The first organization to develop practical nuclear power was the U.S. Navy, with the S1W reactor for the purpose of propelling submarines and aircraft carriers. The first nuclear-powered submarine, USS Nautilus, was put to sea in January 1954.[13][14] The S1W reactor was a pressurized water reactor. This design was chosen because it was simpler, more compact, and easier to operate compared to alternative designs, thus more suitable to be used in submarines. This decision would result in the PWR being the reactor of choice also for power generation, thus having a lasting impact on the civilian electricity market in the years to come.[15]
On June 27, 1954, the Obninsk Nuclear Power Plant in the USSR became the world's first nuclear power plant to generate electricity for a power grid, producing around 5 megawatts of electric power.[16] The world's first commercial nuclear power station, Calder Hall at Windscale, England was connected to the national power grid on 27 August 1956. In common with a number of other generation I reactors, the plant had the dual purpose of producing electricity and plutonium-239, the latter for the nascent nuclear weapons program in Britain.[17]
Expansion and first opposition
The total global installed nuclear capacity initially rose relatively quickly, rising from less than 1 gigawatt (GW) in 1960 to 100 GW in the late 1970s.[13] During the 1970s and 1980s rising economic costs (related to extended construction times largely due to regulatory changes and pressure-group litigation)[18] and falling fossil fuel prices made nuclear power plants then under construction less attractive. In the 1980s in the U.S. and 1990s in Europe, the flat electric grid growth and electricity liberalization also made the addition of large new baseload energy generators economically unattractive.
The 1973 oil crisis had a significant effect on countries, such as France and Japan, which had relied more heavily on oil for electric generation to invest in nuclear power.[19] France would construct 25 nuclear power plants over the next 15 years,[20][21] and as of 2019, 71% of French electricity was generated by nuclear power, the highest percentage by any nation in the world.[22]
Some local opposition to nuclear power emerged in the United States in the early 1960s.[23] In the late 1960s, some members of the scientific community began to express pointed concerns.[24] These anti-nuclear concerns related to nuclear accidents, nuclear proliferation, nuclear terrorism and radioactive waste disposal.[25] In the early 1970s, there were large protests about a proposed nuclear power plant in Wyhl, Germany. The project was cancelled in 1975. The anti-nuclear success at Wyhl inspired opposition to nuclear power in other parts of Europe and North America.[26][27]
By the mid-1970s anti-nuclear activism gained a wider appeal and influence, and nuclear power began to become an issue of major public protest.[28][29] In some countries, the nuclear power conflict "reached an intensity unprecedented in the history of technology controversies".[30][31] The increased public hostility to nuclear power led to a longer license procurement process, more regulations and increased requirements for safety equipment, which made new construction much more expensive.[32][33] In the United States, over 120 Light Water Reactor proposals were ultimately cancelled[34] and the construction of new reactors ground to a halt.[35] The 1979 accident at Three Mile Island with no fatalities, played a major part in the reduction in the number of new plant constructions in many countries.[24]
Chernobyl and renaissance


During the 1980s one new nuclear reactor started up every 17 days on average.[36] By the end of the decade, global installed nuclear capacity reached 300 GW. Since the late 1980s, new capacity additions slowed significantly, with the installed nuclear capacity reaching 366 GW in 2005.
The 1986 Chernobyl disaster in the USSR, involving an RBMK reactor, altered the development of nuclear power and led to a greater focus on meeting international safety and regulatory standards.[37] It is considered the worst nuclear disaster in history both in total casualties, with 56 direct deaths, and financially, with the cleanup and the cost estimated at 18 billion Rbls (US$68 billion in 2019, adjusted for inflation).[38][39] The international organization to promote safety awareness and the professional development of operators in nuclear facilities, the World Association of Nuclear Operators (WANO), was created as a direct outcome of the 1986 Chernobyl accident. The Chernobyl disaster played a major part in the reduction in the number of new plant constructions in the following years.[24] Influenced by these events, Italy voted against nuclear power in a 1987 referendum,[40] becoming the first country to completely phase out nuclear power in 1990.
In the early 2000s, nuclear energy was expecting a nuclear renaissance, an increase in the construction of new reactors, due to concerns about carbon dioxide emissions.[41] During this period, newer generation III reactors, such as the EPR began construction.
- Net electrical generation by source and growth from 1980. In terms of energy generated between 1980 and 2010, the contribution from fission grew the fastest.
- Electricity production in France, showing the shift to nuclear power.thermofossilhydroelectricnuclearOther renewables
- The rate of new reactor constructions essentially halted in the late 1980s. Increased capacity factor in existing reactors was primarily responsible for the continuing increase in electrical energy produced during this period.
- Electricity generation trends in the top producing countries (Our World in Data)
Fukushima accident
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Prospects of a nuclear renaissance were delayed by another nuclear accident.[41][43] The 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident was caused by the Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, one of the largest earthquakes ever recorded. The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant suffered three core meltdowns due to failure of the emergency cooling system for lack of electricity supply. This resulted in the most serious nuclear accident since the Chernobyl disaster.
The accident prompted a re-examination of nuclear safety and nuclear energy policy in many countries.[44] Germany approved plans to close all its reactors by 2022, and many other countries reviewed their nuclear power programs.[45][46][47][48] Following the disaster, Japan shut down all of its nuclear power reactors, some of them permanently, and in 2015 began a gradual process to restart the remaining 40 reactors, following safety checks and based on revised criteria for operations and public approval.[49]
In 2022, the Japanese government, under the leadership of Prime Minister Fumio Kishida, declared that 10 more nuclear power plants were to be reopened since the 2011 disaster.[50] Kishida is also pushing for research and construction of new safer nuclear plants to safeguard Japanese consumers from the fluctuating price of the fossil fuel market and reduce Japan's greenhouse gas emissions.[51] Kishida intends to have Japan become a significant exporter of nuclear energy and technology to developing countries around the world.[51]
Current prospects
By 2015, the IAEA's outlook for nuclear energy had become more promising, recognizing the importance of low-carbon generation for mitigating climate change.[52] As of 2015[update], the global trend was for new nuclear power stations coming online to be balanced by the number of old plants being retired.[53] In 2016, the U.S. Energy Information Administration projected for its "base case" that world nuclear power generation would increase from 2,344 terawatt hours (TWh) in 2012 to 4,500 TWh in 2040. Most of the predicted increase was expected to be in Asia.[54] As of 2018, there were over 150 nuclear reactors planned including 50 under construction.[55] In January 2019, China had 45 reactors in operation, 13 under construction, and planned to build 43 more, which would make it the world's largest generator of nuclear electricity.[56] As of 2021, 17 reactors were reported to be under construction. China built significantly fewer reactors than originally planned. Its share of electricity from nuclear power was 5% in 2019[57] and observers have cautioned that, along with the risks, the changing economics of energy generation may cause new nuclear energy plants to "no longer make sense in a world that is leaning toward cheaper, more reliable renewable energy".[58][59]
In October 2021, the Japanese cabinet approved the new Plan for Electricity Generation to 2030 prepared by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy (ANRE) and an advisory committee, following public consultation. The nuclear target for 2030 requires the restart of another ten reactors. Prime Minister Fumio Kishida in July 2022 announced that the country should consider building advanced reactors and extending operating licences beyond 60 years.[60]
As of 2022, with world oil and gas prices on the rise, while Germany is restarting its coal plants to deal with loss of Russian gas that it needs to supplement its Energiewende,[61] many other countries have announced ambitious plans to reinvigorate ageing nuclear generating capacity with new investments. French President Emmanuel Macron announced his intention to build six new reactors in coming decades, placing nuclear at the heart of France's drive for carbon neutrality by 2050.[62] Meanwhile, in the United States, the Department of Energy, in collaboration with commercial entities, TerraPower and X-energy, is planning on building two different advanced nuclear reactors by 2027, with further plans for nuclear implementation in its long term green energy and energy security goals.[63]
Power plants
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Nuclear power plants are thermal power stations that generate electricity by harnessing the thermal energy released from nuclear fission. A fission nuclear power plant is generally composed of: a nuclear reactor, in which the nuclear reactions generating heat take place; a cooling system, which removes the heat from inside the reactor; a steam turbine, which transforms the heat into mechanical energy; an electric generator, which transforms the mechanical energy into electrical energy.[65]
When a neutron hits the nucleus of a uranium-235 or plutonium atom, it can split the nucleus into two smaller nuclei, which is a nuclear fission reaction. The reaction releases energy and neutrons. The released neutrons can hit other uranium or plutonium nuclei, causing new fission reactions, which release more energy and more neutrons. This is called a chain reaction. In most commercial reactors, the reaction rate is contained by control rods that absorb excess neutrons. The controllability of nuclear reactors depends on the fact that a small fraction of neutrons resulting from fission are delayed. The time delay between the fission and the release of the neutrons slows changes in reaction rates and gives time for moving the control rods to adjust the reaction rate.[65][66]
Fuel cycle

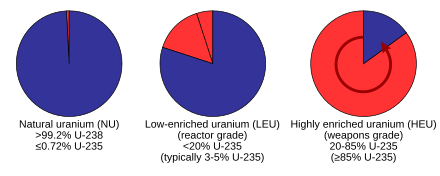
The life cycle of nuclear fuel starts with uranium mining. The uranium ore is then converted into a compact ore concentrate form, known as yellowcake (U3O8), to facilitate transport.[67] Fission reactors generally need uranium-235, a fissile isotope of uranium. The concentration of uranium-235 in natural uranium is low (about 0.7%). Some reactors can use this natural uranium as fuel, depending on their neutron economy. These reactors generally have graphite or heavy water moderators. For light water reactors, the most common type of reactor, this concentration is too low, and it must be increased by a process called uranium enrichment.[67] In civilian light water reactors, uranium is typically enriched to 3.5–5% uranium-235.[68] The uranium is then generally converted into uranium oxide (UO2), a ceramic, that is then compressively sintered into fuel pellets, a stack of which forms fuel rods of the proper composition and geometry for the particular reactor.[68]
After some time in the reactor, the fuel will have reduced fissile material and increased fission products, until its use becomes impractical.[68] At this point, the spent fuel will be moved to a spent fuel pool which provides cooling for the thermal heat and shielding for ionizing radiation. After several months or years, the spent fuel is radioactively and thermally cool enough to be moved to dry storage casks or reprocessed.[68]
Uranium resources
Uranium is a fairly common element in the Earth's crust: it is approximately as common as tin or germanium, and is about 40 times more common than silver.[69] Uranium is present in trace concentrations in most rocks, dirt, and ocean water, but is generally economically extracted only where it is present in relatively high concentrations. Uranium mining can be underground, open-pit, or in-situ leach mining. An increasing number of the highest output mines are remote underground operations, such as McArthur River uranium mine, in Canada, which by itself accounts for 13% of global production. As of 2011 the world's known resources of uranium, economically recoverable at the arbitrary price ceiling of US$130/kg, were enough to last for between 70 and 100 years.[70][71][72] In 2007, the OECD estimated 670 years of economically recoverable uranium in total conventional resources and phosphate ores assuming the then-current use rate.[73]
Light water reactors make relatively inefficient use of nuclear fuel, mostly using only the very rare uranium-235 isotope.[74] Nuclear reprocessing can make this waste reusable, and newer reactors also achieve a more efficient use of the available resources than older ones.[74] With a pure fast reactor fuel cycle with a burn up of all the uranium and actinides (which presently make up the most hazardous substances in nuclear waste), there is an estimated 160,000 years worth of uranium in total conventional resources and phosphate ore at the price of 60–100 US$/kg.[75] However, reprocessing is expensive, possibly dangerous and can be used to manufacture nuclear weapons.[76][77][78][79][80] One analysis found that uranium prices could increase by two orders of magnitude between 2035 and 2100 and that there could be a shortage near the end of the century.[81] A 2017 study by researchers from MIT and WHOI found that "at the current consumption rate, global conventional reserves of terrestrial uranium (approximately 7.6 million tonnes) could be depleted in a little over a century".[82] Limited uranium-235 supply may inhibit substantial expansion with the current nuclear technology.[83] While various ways to reduce dependence on such resources are being explored,[84][85][86] new nuclear technologies are considered to not be available in time for climate change mitigation purposes or competition with alternatives of renewables in addition to being more expensive and require costly research and development.[83][87][88] A study found it to be uncertain whether identified resources will be developed quickly enough to provide uninterrupted fuel supply to expanded nuclear facilities[89] and various forms of mining may be challenged by ecological barriers, costs, and land requirements.[90][91] Researchers also report considerable import dependence of nuclear energy.[92][93][94][95]
Unconventional uranium resources also exist. Uranium is naturally present in seawater at a concentration of about 3 micrograms per liter,[96][97][98] with 4.4 billion tons of uranium considered present in seawater at any time.[99] In 2014 it was suggested that it would be economically competitive to produce nuclear fuel from seawater if the process was implemented at large scale.[100] Like fossil fuels, over geological timescales, uranium extracted on an industrial scale from seawater would be replenished by both river erosion of rocks and the natural process of uranium dissolved from the surface area of the ocean floor, both of which maintain the solubility equilibria of seawater concentration at a stable level.[99] Some commentators have argued that this strengthens the case for nuclear power to be considered a renewable energy.[101]
Waste

The normal operation of nuclear power plants and facilities produce radioactive waste, or nuclear waste. This type of waste is also produced during plant decommissioning. There are two broad categories of nuclear waste: low-level waste and high-level waste.[103] The first has low radioactivity and includes contaminated items such as clothing, which poses limited threat. High-level waste is mainly the spent fuel from nuclear reactors, which is very radioactive and must be cooled and then safely disposed of or reprocessed.[103]
High-level waste


The most important waste stream from nuclear power reactors is spent nuclear fuel, which is considered high-level waste. For Light Water Reactors (LWRs), spent fuel is typically composed of 95% uranium, 4% fission products, and about 1% transuranic actinides (mostly plutonium, neptunium and americium).[105] The fission products are responsible for the bulk of the short-term radioactivity, whereas the plutonium and other transuranics are responsible for the bulk of the long-term radioactivity.[106]
High-level waste (HLW) must be stored isolated from the biosphere with sufficient shielding so as to limit radiation exposure. After being removed from the reactors, used fuel bundles are stored for six to ten years in spent fuel pools, which provide cooling and shielding against radiation. After that, the fuel is cool enough that it can be safely transferred to dry cask storage.[107] The radioactivity decreases exponentially with time, such that it will have decreased by 99.5% after 100 years.[108] The more intensely radioactive short-lived fission products (SLFPs) decay into stable elements in approximately 300 years, and after about 100,000 years, the spent fuel becomes less radioactive than natural uranium ore.[102][109]
Commonly suggested methods to isolate LLFP waste from the biosphere include separation and transmutation,[102] synroc treatments, or deep geological storage.[110][111][112][113]
Thermal-neutron reactors, which presently constitute the majority of the world fleet, cannot burn up the reactor grade plutonium that is generated during the reactor operation. This limits the life of nuclear fuel to a few years. In some countries, such as the United States, spent fuel is classified in its entirety as a nuclear waste.[114] In other countries, such as France, it is largely reprocessed to produce a partially recycled fuel, known as mixed oxide fuel or MOX. For spent fuel that does not undergo reprocessing, the most concerning isotopes are the medium-lived transuranic elements, which are led by reactor-grade plutonium (half-life 24,000 years).[115] Some proposed reactor designs, such as the integral fast reactor and molten salt reactors, can use as fuel the plutonium and other actinides in spent fuel from light water reactors, thanks to their fast fission spectrum. This offers a potentially more attractive alternative to deep geological disposal.[116][117][118]
The thorium fuel cycle results in similar fission products, though creates a much smaller proportion of transuranic elements from neutron capture events within a reactor. Spent thorium fuel, although more difficult to handle than spent uranium fuel, may present somewhat lower proliferation risks.[119]
Low-level waste
The nuclear industry also produces a large volume of low-level waste, with low radioactivity, in the form of contaminated items like clothing, hand tools, water purifier resins, and (upon decommissioning) the materials of which the reactor itself is built. Low-level waste can be stored on-site until radiation levels are low enough to be disposed of as ordinary waste, or it can be sent to a low-level waste disposal site.[120]
Waste relative to other types
In countries with nuclear power, radioactive wastes account for less than 1% of total industrial toxic wastes, much of which remains hazardous for long periods.[74] Overall, nuclear power produces far less waste material by volume than fossil-fuel based power plants.[121] Coal-burning plants, in particular, produce large amounts of toxic and mildly radioactive ash resulting from the concentration of naturally occurring radioactive materials in coal.[122] A 2008 report from Oak Ridge National Laboratory concluded that coal power actually results in more radioactivity being released into the environment than nuclear power operation, and that the population effective dose equivalent from radiation from coal plants is 100 times that from the operation of nuclear plants.[123] Although coal ash is much less radioactive than spent nuclear fuel by weight, coal ash is produced in much higher quantities per unit of energy generated. It is also released directly into the environment as fly ash, whereas nuclear plants use shielding to protect the environment from radioactive materials.[124]
Nuclear waste volume is small compared to the energy produced. For example, at Yankee Rowe Nuclear Power Station, which generated 44 billion kilowatt hours of electricity when in service, its complete spent fuel inventory is contained within sixteen casks.[125] It is estimated that to produce a lifetime supply of energy for a person at a western standard of living (approximately 3 GWh) would require on the order of the volume of a soda can of low enriched uranium, resulting in a similar volume of spent fuel generated.[126][127][128]
Waste disposal

Following interim storage in a spent fuel pool, the bundles of used fuel rod assemblies of a typical nuclear power station are often stored on site in dry cask storage vessels.[129] Presently, waste is mainly stored at individual reactor sites and there are over 430 locations around the world where radioactive material continues to accumulate.
Disposal of nuclear waste is often considered the most politically divisive aspect in the lifecycle of a nuclear power facility.[130] The lack of movement of nuclear waste in the 2 billion year old natural nuclear fission reactors in Oklo, Gabon is cited as "a source of essential information today."[131][132] Experts suggest that centralized underground repositories which are well-managed, guarded, and monitored, would be a vast improvement.[130] There is an "international consensus on the advisability of storing nuclear waste in deep geological repositories".[133] With the advent of new technologies, other methods including horizontal drillhole disposal into geologically inactive areas have been proposed.[134][135]

There are no commercial scale purpose built underground high-level waste repositories in operation.[133][136][137] However, in Finland the Onkalo spent nuclear fuel repository of the Olkiluoto Nuclear Power Plant was under construction as of 2015.[138]
Reprocessing
Most thermal-neutron reactors run on a once-through nuclear fuel cycle, mainly due to the low price of fresh uranium. However, many reactors are also fueled with recycled fissionable materials that remain in spent nuclear fuel. The most common fissionable material that is recycled is the reactor-grade plutonium (RGPu) that is extracted from spent fuel. It is mixed with uranium oxide and fabricated into mixed-oxide or MOX fuel. Because thermal LWRs remain the most common reactor worldwide, this type of recycling is the most common. It is considered to increase the sustainability of the nuclear fuel cycle, reduce the attractiveness of spent fuel to theft, and lower the volume of high level nuclear waste.[139] Spent MOX fuel cannot generally be recycled for use in thermal-neutron reactors. This issue does not affect fast-neutron reactors, which are therefore preferred in order to achieve the full energy potential of the original uranium.[140][141]
The main constituent of spent fuel from LWRs is slightly enriched uranium. This can be recycled into reprocessed uranium (RepU), which can be used in a fast reactor, used directly as fuel in CANDU reactors, or re-enriched for another cycle through an LWR. Re-enriching of reprocessed uranium is common in France and Russia.[142] Reprocessed uranium is also safer in terms of nuclear proliferation potential.[143][144][145]
Reprocessing has the potential to recover up to 95% of the uranium and plutonium fuel in spent nuclear fuel, as well as reduce long-term radioactivity within the remaining waste. However, reprocessing has been politically controversial because of the potential for nuclear proliferation and varied perceptions of increasing the vulnerability to nuclear terrorism.[140][146] Reprocessing also leads to higher fuel cost compared to the once-through fuel cycle.[140][146] While reprocessing reduces the volume of high-level waste, it does not reduce the fission products that are the primary causes of residual heat generation and radioactivity for the first few centuries outside the reactor. Thus, reprocessed waste still requires an almost identical treatment for the initial first few hundred years.
Reprocessing of civilian fuel from power reactors is currently done in France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Japan, and India. In the United States, spent nuclear fuel is currently not reprocessed.[142] The La Hague reprocessing facility in France has operated commercially since 1976 and is responsible for half the world's reprocessing as of 2010.[147] It produces MOX fuel from spent fuel derived from several countries. More than 32,000 tonnes of spent fuel had been reprocessed as of 2015, with the majority from France, 17% from Germany, and 9% from Japan.[148]
Breeding

Breeding is the process of converting non-fissile material into fissile material that can be used as nuclear fuel. The non-fissile material that can be used for this process is called fertile material, and constitute the vast majority of current nuclear waste. This breeding process occurs naturally in breeder reactors. As opposed to light water thermal-neutron reactors, which use uranium-235 (0.7% of all natural uranium), fast-neutron breeder reactors use uranium-238 (99.3% of all natural uranium) or thorium. A number of fuel cycles and breeder reactor combinations are considered to be sustainable or renewable sources of energy.[149][150] In 2006 it was estimated that with seawater extraction, there was likely five billion years' worth of uranium resources for use in breeder reactors.[151]
Breeder technology has been used in several reactors, but as of 2006, the high cost of reprocessing fuel safely requires uranium prices of more than US$200/kg before becoming justified economically.[152] Breeder reactors are however being developed for their potential to burn all of the actinides (the most active and dangerous components) in the present inventory of nuclear waste, while also producing power and creating additional quantities of fuel for more reactors via the breeding process.[153][154] As of 2017, there are two breeders producing commercial power, BN-600 reactor and the BN-800 reactor, both in Russia.[155] The Phénix breeder reactor in France was powered down in 2009 after 36 years of operation.[155] Both China and India are building breeder reactors. The Indian 500 MWe Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor is in the commissioning phase,[156] with plans to build more.[157]
Another alternative to fast-neutron breeders are thermal-neutron breeder reactors that use uranium-233 bred from thorium as fission fuel in the thorium fuel cycle.[158] Thorium is about 3.5 times more common than uranium in the Earth's crust, and has different geographic characteristics.[158] India's three-stage nuclear power programme features the use of a thorium fuel cycle in the third stage, as it has abundant thorium reserves but little uranium.[158]
Decommissioning
Nuclear decommissioning is the process of dismantling a nuclear facility to the point that it no longer requires measures for radiation protection,[159] returning the facility and its parts to a safe enough level to be entrusted for other uses.[160] Due to the presence of radioactive materials, nuclear decommissioning presents technical and economic challenges.[161] The costs of decommissioning are generally spread over the lifetime of a facility and saved in a decommissioning fund.[162]
Production


2021 world electricity generation by source. Total generation was 28 petawatt-hours.[164]
Civilian nuclear power supplied 2,602 terawatt hours (TWh) of electricity in 2023, equivalent to about 9% of global electricity generation,[3] and was the second largest low-carbon power source after hydroelectricity.[165] Nuclear power's contribution to global energy production was about 4% in 2023. This is a little more than wind power, which provided 3.5% of global energy in 2023.[166] Nuclear power's share of global electricity production has fallen from 16.5% in 1997, in large part because the economics of nuclear power have become more difficult.[167]
As of November 2024,[update] there are 415 civilian fission reactors in the world, with a combined electrical capacity of 374 gigawatt (GW).[4] There are also 66 nuclear power reactors under construction and 87 reactors planned, with a combined capacity of 72 GW and 84 GW, respectively.[5] The United States has the largest fleet of nuclear reactors, generating over 800 TWh per year with an average capacity factor of 92%.[168] Most reactors under construction are generation III reactors in Asia.[169]
Regional differences in the use of nuclear power are large. The United States produces the most nuclear energy in the world, with nuclear power providing 19% of the electricity it consumes, while France produces the highest percentage of its electrical energy from nuclear reactors—65% in 2023.[22] In the European Union, nuclear power provides 22% of the electricity as of 2022.[170] Nuclear power is the single largest low-carbon electricity source in the United States,[171] and accounts for about half of the European Union's low-carbon electricity.[170] Nuclear energy policy differs among European Union countries, and some, such as Austria, Estonia, Ireland and Italy, have no active nuclear power stations.
In addition, there were approximately 140 naval vessels using nuclear propulsion in operation, powered by about 180 reactors.[172][173] These include military and some civilian ships, such as nuclear-powered icebreakers.[174]
International research is continuing into additional uses of process heat such as hydrogen production (in support of a hydrogen economy), for desalinating sea water, and for use in district heating systems.[175]
Economics
The economics of new nuclear power plants is a controversial subject and multi-billion-dollar investments depend on the choice of energy sources. Nuclear power plants typically have high capital costs for building the plant. For this reason, comparison with other power generation methods is strongly dependent on assumptions about construction timescales and capital financing for nuclear plants. Fuel costs account for about 30 percent of the operating costs, while prices are subject to the market.[176]
The high cost of construction is one of the biggest challenges for nuclear power plants. A new 1,100 MW plant is estimated to cost between US$6 billion to US$9 billion.[177] Nuclear power cost trends show large disparity by nation, design, build rate and the establishment of familiarity in expertise. The only two nations for which data is available that saw cost decreases in the 2000s were India and South Korea.[178]
Analysis of the economics of nuclear power must also take into account who bears the risks of future uncertainties. As of 2010, all operating nuclear power plants have been developed by state-owned or regulated electric utility monopolies.[179] Many countries have since liberalized the electricity market where these risks, and the risk of cheaper competitors emerging before capital costs are recovered, are borne by plant suppliers and operators rather than consumers, which leads to a significantly different evaluation of the economics of new nuclear power plants.[180]
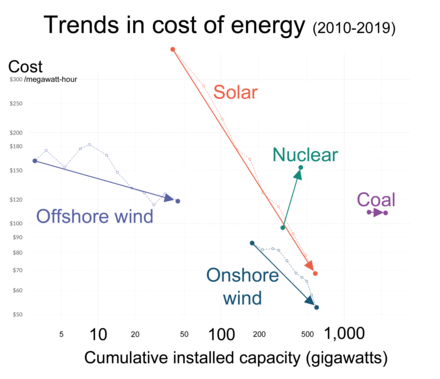
The levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) from a new nuclear power plant is estimated to be 69 USD/MWh, according to an analysis by the International Energy Agency and the OECD Nuclear Energy Agency. This represents the median cost estimate for an nth-of-a-kind nuclear power plant to be completed in 2025, at a discount rate of 7%. Nuclear power was found to be the least-cost option among dispatchable technologies.[181] Variable renewables can generate cheaper electricity: the median cost of onshore wind power was estimated to be 50 USD/MWh, and utility-scale solar power 56 USD/MWh.[181] At the assumed CO2 emission cost of 30 USD/ton, power from coal (88 USD/MWh) and gas (71 USD/MWh) is more expensive than low-carbon technologies. Electricity from long-term operation of nuclear power plants by lifetime extension was found to be the least-cost option, at 32 USD/MWh.[181]
Measures to mitigate global warming, such as a carbon tax or carbon emissions trading, may favor the economics of nuclear power.[182][183] Extreme weather events, including events made more severe by climate change, are decreasing all energy source reliability including nuclear energy by a small degree, depending on location siting.[184][185]
New small modular reactors, such as those developed by NuScale Power, are aimed at reducing the investment costs for new construction by making the reactors smaller and modular, so that they can be built in a factory.
Certain designs had considerable early positive economics, such as the CANDU, which realized a much higher capacity factor and reliability when compared to generation II light water reactors up to the 1990s.[186]
Nuclear power plants, though capable of some grid-load following, are typically run as much as possible to keep the cost of the generated electrical energy as low as possible, supplying mostly base-load electricity.[187] Due to the on-line refueling reactor design, PHWRs (of which the CANDU design is a part) continue to hold many world record positions for longest continual electricity generation, often over 800 days.[188] The specific record as of 2019 is held by a PHWR at Kaiga Atomic Power Station, generating electricity continuously for 962 days.[189]
Costs not considered in LCOE calculations include funds for research and development, and disasters (the Fukushima disaster is estimated to cost taxpayers ≈$187 billion).[190] In some cases, Governments were found to force "consumers to pay upfront for potential cost overruns"[88] or subsidize uneconomic nuclear energy[191] or be required to do so.[59] Nuclear operators are liable to pay for the waste management in the European Union.[192] In the U.S., the Congress reportedly decided 40 years ago that the nation, and not private companies, would be responsible for storing radioactive waste with taxpayers paying for the costs.[193] The World Nuclear Waste Report 2019 found that "even in countries in which the polluter-pays-principle is a legal requirement, it is applied incompletely" and notes the case of the German Asse II deep geological disposal facility, where the retrieval of large amounts of waste has to be paid for by taxpayers.[194] Similarly, other forms of energy, including fossil fuels and renewables, have a portion of their costs covered by governments.[195]
Use in space

The most common use of nuclear power in space is the use of radioisotope thermoelectric generators, which use radioactive decay to generate power. These power generators are relatively small scale (few kW), and they are mostly used to power space missions and experiments for long periods where solar power is not available in sufficient quantity, such as in the Voyager 2 space probe.[196] A few space vehicles have been launched using nuclear reactors: 34 reactors belong to the Soviet RORSAT series and one was the American SNAP-10A.[196]
Both fission and fusion appear promising for space propulsion applications, generating higher mission velocities with less reaction mass.[196][197]
Safety

Nuclear power plants have three unique characteristics that affect their safety, as compared to other power plants. Firstly, intensely radioactive materials are present in a nuclear reactor. Their release to the environment could be hazardous. Secondly, the fission products, which make up most of the intensely radioactive substances in the reactor, continue to generate a significant amount of decay heat even after the fission chain reaction has stopped. If the heat cannot be removed from the reactor, the fuel rods may overheat and release radioactive materials. Thirdly, a criticality accident (a rapid increase of the reactor power) is possible in certain reactor designs if the chain reaction cannot be controlled. These three characteristics have to be taken into account when designing nuclear reactors.[198]
All modern reactors are designed so that an uncontrolled increase of the reactor power is prevented by natural feedback mechanisms, a concept known as negative void coefficient of reactivity. If the temperature or the amount of steam in the reactor increases, the fission rate inherently decreases. The chain reaction can also be manually stopped by inserting control rods into the reactor core. Emergency core cooling systems (ECCS) can remove the decay heat from the reactor if normal cooling systems fail.[199] If the ECCS fails, multiple physical barriers limit the release of radioactive materials to the environment even in the case of an accident. The last physical barrier is the large containment building.[198]
With a death rate of 0.03 per TWh, nuclear power is the second safest energy source per unit of energy generated, after solar power, in terms of mortality when the historical track-record is considered.[200] Energy produced by coal, petroleum, natural gas and hydropower has caused more deaths per unit of energy generated due to air pollution and energy accidents. This is found when comparing the immediate deaths from other energy sources to both the immediate and the latent, or predicted, indirect cancer deaths from nuclear energy accidents.[201][202] When the direct and indirect fatalities (including fatalities resulting from the mining and air pollution) from nuclear power and fossil fuels are compared,[203] the use of nuclear power has been calculated to have prevented about 1.84 million deaths from air pollution between 1971 and 2009, by reducing the proportion of energy that would otherwise have been generated by fossil fuels.[204][205] Following the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, it has been estimated that if Japan had never adopted nuclear power, accidents and pollution from coal or gas plants would have caused more lost years of life.[206]
Serious impacts of nuclear accidents are often not directly attributable to radiation exposure, but rather social and psychological effects. Evacuation and long-term displacement of affected populations created problems for many people, especially the elderly and hospital patients.[207] Forced evacuation from a nuclear accident may lead to social isolation, anxiety, depression, psychosomatic medical problems, reckless behavior, and suicide. A comprehensive 2005 study on the aftermath of the Chernobyl disaster concluded that the mental health impact is the largest public health problem caused by the accident.[208] Frank N. von Hippel, an American scientist, commented that a disproportionate fear of ionizing radiation (radiophobia) could have long-term psychological effects on the population of contaminated areas following the Fukushima disaster.[209]
Accidents


Some serious nuclear and radiation accidents have occurred. The severity of nuclear accidents is generally classified using the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES) introduced by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). The scale ranks anomalous events or accidents on a scale from 0 (a deviation from normal operation that poses no safety risk) to 7 (a major accident with widespread effects). There have been three accidents of level 5 or higher in the civilian nuclear power industry, two of which, the Chernobyl accident and the Fukushima accident, are ranked at level 7.
The first major nuclear accidents were the Kyshtym disaster in the Soviet Union and the Windscale fire in the United Kingdom, both in 1957. The first major accident at a nuclear reactor in the USA occurred in 1961 at the SL-1, a U.S. Army experimental nuclear power reactor at the Idaho National Laboratory. An uncontrolled chain reaction resulted in a steam explosion which killed the three crew members and caused a meltdown.[212][213] Another serious accident happened in 1968, when one of the two liquid-metal-cooled reactors on board the Soviet submarine K-27 underwent a fuel element failure, with the emission of gaseous fission products into the surrounding air, resulting in 9 crew fatalities and 83 injuries.[214]
The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident was caused by the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami. The accident has not caused any radiation-related deaths but resulted in radioactive contamination of surrounding areas. The difficult cleanup operation is expected to cost tens of billions of dollars over 40 or more years.[215][216] The Three Mile Island accident in 1979 was a smaller scale accident, rated at INES level 5. There were no direct or indirect deaths caused by the accident.[217]
The impact of nuclear accidents is controversial. According to Benjamin K. Sovacool, fission energy accidents ranked first among energy sources in terms of their total economic cost, accounting for 41% of all property damage attributed to energy accidents.[218] Another analysis found that coal, oil, liquid petroleum gas and hydroelectric accidents (primarily due to the Banqiao Dam disaster) have resulted in greater economic impacts than nuclear power accidents.[219] The study compares latent cancer deaths attributable to nuclear power with immediate deaths from other energy sources per unit of energy generated, and does not include fossil fuel related cancer and other indirect deaths created by the use of fossil fuel consumption in its "severe accident" (an accident with more than five fatalities) classification. The Chernobyl accident in 1986 caused approximately 50 deaths from direct and indirect effects, and some temporary serious injuries from acute radiation syndrome.[220] The future predicted mortality from increases in cancer rates is estimated at 4000 in the decades to come.[221][222][223] However, the costs have been large and are increasing.
Nuclear power works under an insurance framework that limits or structures accident liabilities in accordance with national and international conventions.[224] It is often argued that this potential shortfall in liability represents an external cost not included in the cost of nuclear electricity. This cost is small, amounting to about 0.1% of the levelized cost of electricity, according to a study by the Congressional Budget Office in the United States.[225] These beyond-regular insurance costs for worst-case scenarios are not unique to nuclear power. Hydroelectric power plants are similarly not fully insured against a catastrophic event such as dam failures. For example, the failure of the Banqiao Dam caused the death of an estimated 30,000 to 200,000 people, and 11 million people lost their homes. As private insurers base dam insurance premiums on limited scenarios, major disaster insurance in this sector is likewise provided by the state.[226]
Attacks and sabotage
Terrorists could target nuclear power plants in an attempt to release radioactive contamination into the community. The United States 9/11 Commission has said that nuclear power plants were potential targets originally considered for the September 11, 2001 attacks. An attack on a reactor's spent fuel pool could also be serious, as these pools are less protected than the reactor core. The release of radioactivity could lead to thousands of near-term deaths and greater numbers of long-term fatalities.[227]
In the United States, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission carries out "Force on Force" (FOF) exercises at all nuclear power plant sites at least once every three years.[227] In the United States, plants are surrounded by a double row of tall fences which are electronically monitored. The plant grounds are patrolled by a sizeable force of armed guards.[228]
Insider sabotage is also a threat because insiders can observe and work around security measures. Successful insider crimes depended on the perpetrators' observation and knowledge of security vulnerabilities.[229] A fire caused 5–10 million dollars worth of damage to New York's Indian Point Energy Center in 1971.[230] The arsonist was a plant maintenance worker.[231]
Proliferation


Nuclear proliferation is the spread of nuclear weapons, fissionable material, and weapons-related nuclear technology to states that do not already possess nuclear weapons. Many technologies and materials associated with the creation of a nuclear power program have a dual-use capability, in that they can also be used to make nuclear weapons. For this reason, nuclear power presents proliferation risks.
Nuclear power program can become a route leading to a nuclear weapon. An example of this is the concern over Iran's nuclear program.[234] The re-purposing of civilian nuclear industries for military purposes would be a breach of the Non-Proliferation Treaty, to which 190 countries adhere. As of April 2012, there are thirty one countries that have civil nuclear power plants,[235] of which nine have nuclear weapons. The vast majority of these nuclear weapons states have produced weapons before commercial nuclear power stations.
A fundamental goal for global security is to minimize the nuclear proliferation risks associated with the expansion of nuclear power.[234] The Global Nuclear Energy Partnership was an international effort to create a distribution network in which developing countries in need of energy would receive nuclear fuel at a discounted rate, in exchange for that nation agreeing to forgo their own indigenous development of a uranium enrichment program. The France-based Eurodif/European Gaseous Diffusion Uranium Enrichment Consortium is a program that successfully implemented this concept, with Spain and other countries without enrichment facilities buying a share of the fuel produced at the French-controlled enrichment facility, but without a transfer of technology.[236] Iran was an early participant from 1974 and remains a shareholder of Eurodif via Sofidif.
A 2009 United Nations report said that:
the revival of interest in nuclear power could result in the worldwide dissemination of uranium enrichment and spent fuel reprocessing technologies, which present obvious risks of proliferation as these technologies can produce fissile materials that are directly usable in nuclear weapons.[237]
On the other hand, power reactors can also reduce nuclear weapon arsenals when military-grade nuclear materials are reprocessed to be used as fuel in nuclear power plants. The Megatons to Megawatts Program is considered the single most successful non-proliferation program to date.[232] Up to 2005, the program had processed $8 billion of high enriched, weapons-grade uranium into low enriched uranium suitable as nuclear fuel for commercial fission reactors by diluting it with natural uranium. This corresponds to the elimination of 10,000 nuclear weapons.[238] For approximately two decades, this material generated nearly 10 percent of all the electricity consumed in the United States, or about half of all U.S. nuclear electricity, with a total of around 7,000 TWh of electricity produced.[239] In total it is estimated to have cost $17 billion, a "bargain for US ratepayers", with Russia profiting $12 billion from the deal.[239] Much needed profit for the Russian nuclear oversight industry, which after the collapse of the Soviet economy, had difficulties paying for the maintenance and security of the Russian Federations highly enriched uranium and warheads.[240] The Megatons to Megawatts Program was hailed as a major success by anti-nuclear weapon advocates as it has largely been the driving force behind the sharp reduction in the number of nuclear weapons worldwide since the cold war ended.[232] However, without an increase in nuclear reactors and greater demand for fissile fuel, the cost of dismantling and down blending has dissuaded Russia from continuing their disarmament. As of 2013, Russia appears to not be interested in extending the program.[241]
Environmental impact

Being a low-carbon energy source with relatively little land-use requirements, nuclear energy can have a positive environmental impact. It also requires a constant supply of significant amounts of water and affects the environment through mining and milling.[242][243][244][245] Its largest potential negative impacts on the environment may arise from its transgenerational risks for nuclear weapons proliferation that may increase risks of their use in the future, risks for problems associated with the management of the radioactive waste such as groundwater contamination, risks for accidents and for risks for various forms of attacks on waste storage sites or reprocessing- and power-plants.[76][246][247][248][249][245][250][251] However, these remain mostly only risks as historically there have only been few disasters at nuclear power plants with known relatively substantial environmental impacts.
Carbon emissions
| Part of a series on |
| Climate change mitigation |
|---|

Nuclear power is one of the leading low carbon power generation methods of producing electricity, and in terms of total life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions per unit of energy generated, has emission values comparable to or lower than renewable energy.[253][254] A 2014 analysis of the carbon footprint literature by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reported that the embodied total life-cycle emission intensity of nuclear power has a median value of 12 g CO2eq/kWh, which is the lowest among all commercial baseload energy sources.[252][255] This is contrasted with coal and natural gas at 820 and 490 g CO2 eq/kWh.[252][255] As of 2021, nuclear reactors worldwide have helped avoid the emission of 72 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide since 1970, compared to coal-fired electricity generation, according to a report.[205][256]
Radiation
The average dose from natural background radiation is 2.4 millisievert per year (mSv/a) globally. It varies between 1 mSv/a and 13 mSv/a, depending mostly on the geology of the location. According to the United Nations (UNSCEAR), regular nuclear power plant operations, including the nuclear fuel cycle, increases this amount by 0.0002 mSv/a of public exposure as a global average. The average dose from operating nuclear power plants to the local populations around them is less than 0.0001 mSv/a.[257] For comparison, the average dose to those living within 50 miles (80 km) of a coal power plant is over three times this dose, at 0.0003 mSv/a.[258]
Chernobyl resulted in the most affected surrounding populations and male recovery personnel receiving an average initial 50 to 100 mSv over a few hours to weeks, while the remaining global legacy of the worst nuclear power plant accident in average exposure is 0.002 mSv/a and is continuously dropping at the decaying rate, from the initial high of 0.04 mSv per person averaged over the entire populace of the Northern Hemisphere in the year of the accident in 1986.[257]
Debate
LCOE is a measure of the average net present cost of electricity generation for a generating plant over its lifetime. As a metric, it remains controversial as the lifespan of units are not independent but manufacturer projections, not a demonstrated longevity.
The nuclear power debate concerns the controversy which has surrounded the deployment and use of nuclear fission reactors to generate electricity from nuclear fuel for civilian purposes.[29][260][30]
Proponents of nuclear energy regard it as a sustainable energy source that reduces carbon emissions and increases energy security by decreasing dependence on other energy sources that are also[93][94][95] often dependent on imports.[261][262][263] For example, proponents note that annually, nuclear-generated electricity reduces 470 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions that would otherwise come from fossil fuels.[264] Additionally, the amount of comparatively low waste that nuclear energy does create is safely disposed of by the large scale nuclear energy production facilities or it is repurposed/recycled for other energy uses.[265] M. King Hubbert, who popularized the concept of peak oil, saw oil as a resource that would run out and considered nuclear energy its replacement.[266] Proponents also claim that the present quantity of nuclear waste is small and can be reduced through the latest technology of newer reactors and that the operational safety record of fission-electricity in terms of deaths is so far "unparalleled".[18] Kharecha and Hansen estimated that "global nuclear power has prevented an average of 1.84 million air pollution-related deaths and 64 gigatonnes of CO2-equivalent (GtCO2-eq) greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that would have resulted from fossil fuel burning" and, if continued, it could prevent up to 7 million deaths and 240 GtCO2-eq emissions by 2050.[205]
Proponents also bring to attention the opportunity cost of using other forms of electricity. For example, the Environmental Protection Agency estimates that coal kills 30,000 people a year,[267] as a result of its environmental impact, while 60 people died in the Chernobyl disaster.[268] A real world example of impact provided by proponents is the 650,000 ton increase in carbon emissions in the two months following the closure of the Vermont Yankee nuclear plant.[269]
Opponents believe that nuclear power poses many threats to people's health and environment[270][271] such as the risk of nuclear weapons proliferation, long-term safe waste management and terrorism in the future.[272][273] They also contend that nuclear power plants are complex systems where many things can and have gone wrong.[274][275] Costs of the Chernobyl disaster amount to ≈$68 billion as of 2019 and are increasing,[38] the Fukushima disaster is estimated to cost taxpayers ~$187 billion,[190] and radioactive waste management is estimated to cost the Eureopean Union nuclear operators ~$250 billion by 2050.[192] However, in countries that already use nuclear energy, when not considering reprocessing, intermediate nuclear waste disposal costs could be relatively fixed to certain but unknown degrees[276] "as the main part of these costs stems from the operation of the intermediate storage facility".[277]
Critics find that one of the largest drawbacks to building new nuclear fission power plants are the large construction and operating costs when compared to alternatives of sustainable energy sources.[58][278][87][244][279] Further costs include ongoing research and development, expensive reprocessing in cases where such is practiced[76][77][78][80] and decommissioning.[280][281][282] Proponents note that focussing on the levelized cost of energy (LCOE), however, ignores the value premium associated with 24/7 dispatchable electricity and the cost of storage and backup systems necessary to integrate variable energy sources into a reliable electrical grid.[283] "Nuclear thus remains the dispatchable low-carbon technology with the lowest expected costs in 2025. Only large hydro reservoirs can provide a similar contribution at comparable costs but remain highly dependent on the natural endowments of individual countries."[284]

Overall, many opponents find that nuclear energy cannot meaningfully contribute to climate change mitigation. In general, they find it to be, too dangerous, too expensive, to take too long for deployment, to be an obstacle to achieving a transition towards sustainability and carbon-neutrality,[87][285][286][287] effectively being a distracting[288][289] competition for resources (i.e. human, financial, time, infrastructure and expertise) for the deployment and development of alternative, sustainable, energy system technologies[88][289][87][290] (such as for wind, ocean and solar[87] – including e.g. floating solar – as well as ways to manage their intermittency other than nuclear baseload[291] generation such as dispatchable generation, renewables-diversification,[292][293] super grids, flexible energy demand and supply regulating smart grids and energy storage[294][295][296][297][298] technologies).[299][300][301][302][303][304][305][306][251]
Nevertheless, there is ongoing research and debate over costs of new nuclear, especially in regions where i.a. seasonal energy storage is difficult to provide and which aim to phase out fossil fuels in favor of low carbon power faster than the global average.[307] Some find that financial transition costs for a 100% renewables-based European energy system that has completely phased out nuclear energy could be more costly by 2050 based on current technologies (i.e. not considering potential advances in e.g. green hydrogen, transmission and flexibility capacities, ways to reduce energy needs, geothermal energy and fusion energy) when the grid only extends across Europe.[308] Arguments of economics and safety are used by both sides of the debate.
Comparison with renewable energy
Slowing global warming requires a transition to a low-carbon economy, mainly by burning far less fossil fuel. Limiting global warming to 1.5 °C is technically possible if no new fossil fuel power plants are built from 2019.[309] This has generated considerable interest and dispute in determining the best path forward to rapidly replace fossil-based fuels in the global energy mix,[310][311] with intense academic debate.[312][313] Sometimes the IEA says that countries without nuclear should develop it as well as their renewable power.[314]
World total primary energy supply of 162,494 TWh (or 13,792 Mtoe) by fuels in 2017 (IEA, 2019)[315]: 6, 8
Several studies suggest that it might be theoretically possible to cover a majority of world energy generation with new renewable sources. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has said that if governments were supportive, renewable energy supply could account for close to 80% of the world's energy use by 2050.[316] While in developed nations the economically feasible geography for new hydropower is lacking, with every geographically suitable area largely already exploited,[317] some proponents of wind and solar energy claim these resources alone could eliminate the need for nuclear power.[313][318]
Nuclear power is comparable to, and in some cases lower, than many renewable energy sources in terms of lives lost in the past per unit of electricity delivered.[203][201][319] Depending on recycling of renewable energy technologies, nuclear reactors may produce a much smaller volume of waste, although much more toxic, expensive to manage and longer-lived.[320][247] A nuclear plant also needs to be disassembled and removed and much of the disassembled nuclear plant needs to be stored as low-level nuclear waste for a few decades.[321] The disposal and management of the wide variety[322] of radioactive waste, of which there are over one quarter of a million tons as of 2018, can cause future damage and costs across the world for over or during hundreds of thousands of years[323][324][325] – possibly over a million years,[326][327][328][329] due to issues such as leakage,[330] malign retrieval, vulnerability to attacks (including of reprocessing[79][76] and power plants), groundwater contamination, radiation and leakage to above ground, brine leakage or bacterial corrosion.[331][326][332][333] The European Commission Joint Research Centre found that as of 2021 the necessary technologies for geological disposal of nuclear waste are now available and can be deployed.[334] Corrosion experts noted in 2020 that putting the problem of storage off any longer "isn't good for anyone".[335] Separated plutonium and enriched uranium could be used for nuclear weapons, which – even with the current centralized control (e.g. state-level) and level of prevalence – are considered to be a difficult and substantial global risk for substantial future impacts on human health, lives, civilization and the environment.[76][246][247][248][249]
Speed of transition and investment needed
Analysis in 2015 by professor Barry W. Brook and colleagues found that nuclear energy could displace or remove fossil fuels from the electric grid completely within 10 years. This finding was based on the historically modest and proven rate at which nuclear energy was added in France and Sweden during their building programs in the 1980s.[336][337] In a similar analysis, Brook had earlier determined that 50% of all global energy, including transportation synthetic fuels etc., could be generated within approximately 30 years if the global nuclear fission build rate was identical to historical proven installation rates calculated in GW per year per unit of global GDP (GW/year/$).[338] This is in contrast to the conceptual studies for 100% renewable energy systems, which would require an order of magnitude more costly global investment per year, which has no historical precedent.[339] These renewable scenarios would also need far greater land devoted to onshore wind and onshore solar projects.[338][339] Brook notes that the "principal limitations on nuclear fission are not technical, economic or fuel-related, but are instead linked to complex issues of societal acceptance, fiscal and political inertia, and inadequate critical evaluation of the real-world constraints facing [the other] low-carbon alternatives."[338]
Scientific data indicates that – assuming 2021 emissions levels – humanity only has a carbon budget equivalent to 11 years of emissions left for limiting warming to 1.5 °C[340][341] while the construction of new nuclear reactors took a median of 7.2–10.9 years in 2018–2020,[333] substantially longer than, alongside other measures, scaling up the deployment of wind and solar – especially for novel reactor types – as well as being more risky, often delayed and more dependent on state-support.[342][343][286][288][87][344][299] Researchers have cautioned that novel nuclear technologies – which have been in development since decades,[345][87][278] are less tested, have higher proliferation risks, have more new safety problems, are often far from commercialization and are more expensive[278][87][244][346] – are not available in time.[83][88][347][288][348][298][349] Critics of nuclear energy often only oppose nuclear fission energy but not nuclear fusion; however, fusion energy is unlikely to be commercially widespread before 2050.[350][351][352][353][354]
Land use
The median land area used by US nuclear power stations per 1 GW installed capacity is 1.3 square miles (3.4 km2).[355][356] To generate the same amount of electricity annually (taking into account capacity factors) from solar PV would require about 60 square miles (160 km2), and from a wind farm about 310 square miles (800 km2).[355][356] Not included in this, is land required for the associated transmission lines, water supply, rail lines, mining and processing of nuclear fuel, and for waste disposal.[357]
Research
Advanced fission reactor designs
Current fission reactors in operation around the world are second or third generation systems, with most of the first-generation systems having been already retired. Research into advanced generation IV reactor types was officially started by the Generation IV International Forum (GIF) based on eight technology goals, including to improve economics, safety, proliferation resistance, natural resource use and the ability to consume existing nuclear waste in the production of electricity. Most of these reactors differ significantly from current operating light water reactors, and are expected to be available for commercial construction after 2030.[358]
Hybrid fusion-fission
Hybrid nuclear power is a proposed means of generating power by the use of a combination of nuclear fusion and fission processes. The concept dates to the 1950s and was briefly advocated by Hans Bethe during the 1970s, but largely remained unexplored until a revival of interest in 2009, due to delays in the realization of pure fusion. When a sustained nuclear fusion power plant is built, it has the potential to be capable of extracting all the fission energy that remains in spent fission fuel, reducing the volume of nuclear waste by orders of magnitude, and more importantly, eliminating all actinides present in the spent fuel, substances which cause security concerns.[359]
Fusion

Nuclear fusion reactions have the potential to be safer and generate less radioactive waste than fission.[360][361] These reactions appear potentially viable, though technically quite difficult and have yet to be created on a scale that could be used in a functional power plant. Fusion power has been under theoretical and experimental investigation since the 1950s. Nuclear fusion research is underway but fusion energy is not likely to be commercially widespread before 2050.[362][363][364]
Several experimental nuclear fusion reactors and facilities exist. The largest and most ambitious international nuclear fusion project currently in progress is ITER, a large tokamak under construction in France. ITER is planned to pave the way for commercial fusion power by demonstrating self-sustained nuclear fusion reactions with positive energy gain. Construction of the ITER facility began in 2007, but the project has run into many delays and budget overruns. The facility is now not expected to begin operations until the year 2027 – 11 years after initially anticipated.[365] A follow on commercial nuclear fusion power station, DEMO, has been proposed.[350][366] There are also suggestions for a power plant based upon a different fusion approach, that of an inertial fusion power plant.
Fusion-powered electricity generation was initially believed to be readily achievable, as fission-electric power had been. However, the extreme requirements for continuous reactions and plasma containment led to projections being extended by several decades. In 2020, more than 80 years after the first attempts, commercialization of fusion power production was thought to be unlikely before 2050.[350][351][352][353][354]
To enhance and accelerate the development of fusion energy, the United States Department of Energy (DOE) granted $46 million to eight firms, including Commonwealth Fusion Systems and Tokamak Energy Inc, in 2023. This ambitious initiative aims to introduce pilot-scale fusion within a decade.[367]
See also
References
- ^ "Power: Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators - NASA Science". science.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2024-10-01.
- ^ Moynihan, M., & Bortz, A. B. (2023). Fusion’s Promise: How Technological Breakthroughs in Nuclear Fusion Can Conquer Climate Change on Earth (And Carry Humans To Mars, Too) [Book]. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22906-0
- ^ a b World Nuclear Performance Report 2024 (PDF) (Report). World Nuclear Association. 2024. pp. 3–5. Retrieved 2024-11-10.
- ^ a b c "Power Reactor Information System". International Atomic Energy Agency. Retrieved 2024-11-10.
- ^ a b "World Nuclear Power Reactors & Uranium Requirements". World Nuclear Association. Retrieved 2024-11-10.
- ^ "Reactors: Modern-Day Alchemy - Argonne's Nuclear Science and Technology Legacy". www.ne.anl.gov. Retrieved 24 March 2021.
- ^ Wellerstein, Alex (2008). "Inside the atomic patent office". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. 64 (2): 26–31. Bibcode:2008BuAtS..64b..26W. doi:10.2968/064002008. ISSN 0096-3402.
- ^ "The Einstein Letter". Atomicarchive.com. Archived from the original on 2013-06-28. Retrieved 2013-06-22.
- ^ "Nautilus (SSN-571)". US Naval History and Heritage Command (US Navy).
- ^ Wendt, Gerald; Geddes, Donald Porter (1945). The Atomic Age Opens. New York: Pocket Books. Archived from the original on 2016-03-28. Retrieved 2017-11-03.
- ^ "Reactors Designed by Argonne National Laboratory: Fast Reactor Technology". U.S. Department of Energy, Argonne National Laboratory. 2012. Archived from the original on 2021-04-18. Retrieved 2012-07-25.
- ^ "Reactor Makes Electricity". Popular Mechanics. Hearst Magazines. March 1952. p. 105.
- ^ a b "50 Years of Nuclear Energy" (PDF). International Atomic Energy Agency. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2010-01-07. Retrieved 2006-11-09.
- ^ "STR (Submarine Thermal Reactor) in "Reactors Designed by Argonne National Laboratory: Light Water Reactor Technology Development"". U.S. Department of Energy, Argonne National Laboratory. 2012. Archived from the original on 2012-06-22. Retrieved 2012-07-25.
- ^ Rockwell, Theodore (1992). The Rickover Effect. Naval Institute Press. p. 162. ISBN 978-1-55750-702-0.
- ^ "From Obninsk Beyond: Nuclear Power Conference Looks to Future". International Atomic Energy Agency. 2004-06-23. Archived from the original on 2006-11-15. Retrieved 2006-06-27.
- ^ Hill, C. N. (2013). An atomic empire: a technical history of the rise and fall of the British atomic energy programme. London, England: Imperial College Press. ISBN 978-1-908977-43-4.
- ^ a b Bernard L. Cohen (1990). The Nuclear Energy Option: An Alternative for the 90s. New York: Plenum Press. ISBN 978-0-306-43567-6.
- ^ Beder, Sharon (2006). "The Japanese Situation, English version of conclusion of Sharon Beder, "Power Play: The Fight to Control the World's Electricity"". Soshisha, Japan. Archived from the original on 2011-03-17. Retrieved 2009-05-15.
- ^ Palfreman, Jon (1997). "Why the French Like Nuclear Energy". Frontline. Public Broadcasting Service. Archived from the original on 25 August 2007. Retrieved 25 August 2007.
- ^ de Preneuf, Rene. "Nuclear Power in France – Why does it Work?". Archived from the original on 13 August 2007. Retrieved 25 August 2007.
- ^ a b "Nuclear Share of Electricity Generation in 2023". Power Reactor Information System. International Atomic Energy Agency. Retrieved 2024-11-11.
- ^ Garb, Paula (1999). "Review of Critical Masses: Opposition to Nuclear Power in California, 1958–1978". Journal of Political Ecology. 6. Archived from the original on 2018-06-01. Retrieved 2011-03-14.
- ^ a b c Rüdig, Wolfgang, ed. (1990). Anti-nuclear Movements: A World Survey of Opposition to Nuclear Energy. Detroit, Michigan: Longman Current Affairs. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-8103-9000-3.
- ^ Martin, Brian (2007). "Opposing nuclear power: past and present". Social Alternatives. 26 (2): 43–47. Archived from the original on 2019-05-10. Retrieved 2011-03-14.
- ^ Mills, Stephen; Williams, Roger (1986). Public acceptance of new technologies: an international review. London: Croom Helm. pp. 375–376. ISBN 978-0-7099-4319-8.
- ^ Robert Gottlieb (2005). Forcing the Spring: The Transformation of the American Environmental Movement, Revised Edition, Island Press, p. 237.
- ^ Falk, Jim (1982). Global Fission: The Battle Over Nuclear Power. Melbourne, Australia: Oxford University Press. pp. 95–96. ISBN 978-0-19-554315-5.
- ^ a b Walker, J. Samuel (2004). Three Mile Island: A Nuclear Crisis in Historical Perspective Archived 2023-03-23 at the Wayback Machine (Berkeley, California: University of California Press), pp. 10–11.
- ^ a b Herbert P. Kitschelt (1986). "Political Opportunity and Political Protest: Anti-Nuclear Movements in Four Democracies" (PDF). British Journal of Political Science. 16 (1): 57. doi:10.1017/s000712340000380x. S2CID 154479502. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2010-08-21. Retrieved 2010-02-28.
- ^ Kitschelt, Herbert P. (1986). "Political Opportunity and Political Protest: Anti-Nuclear Movements in Four Democracies" (PDF). British Journal of Political Science. 16 (1): 71. doi:10.1017/s000712340000380x. S2CID 154479502. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2010-08-21. Retrieved 2010-02-28.
- ^ "Costs of Nuclear Power Plants – What Went Wrong?". www.phyast.pitt.edu. Archived from the original on 2010-04-13. Retrieved 2007-12-04.
- ^ Ginn, Vance; Raia, Elliott (August 18, 2017). "nuclear energy may soon be free from its tangled regulatory web". Washington Examiner. Archived from the original on January 6, 2019. Retrieved January 6, 2019.
- ^ "Nuclear Power: Outlook for New U.S. Reactors" (PDF). p. 3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 2015-10-18.
- ^ Cook, James (1985-02-11). "Nuclear Follies". Forbes Magazine.
- ^ Thorpe, Gary S. (2015). AP Environmental Science, 6th ed. Barrons Educational Series. ISBN 978-1-4380-6728-5. ISBN 1-4380-6728-3
- ^ "Chernobyl Nuclear Accident". www.iaea.org. IAEA. 14 May 2014. Archived from the original on 11 June 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2021.
- ^ a b "Chernobyl: Assessment of Radiological and Health Impact, 2002 update; Chapter II – The release, dispersion and deposition of radionuclides" (PDF). OECD-NEA. 2002. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 June 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ Johnson, Thomas (author/director) (2006). The battle of Chernobyl. Play Film / Discovery Channel. Archived from the original on 2021-03-07. Retrieved 2021-03-23. (see 1996 interview with Mikhail Gorbachev.)
- ^ Sassoon, Donald (2014-06-03). Contemporary Italy: Politics, Economy and Society Since 1945. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-89377-6.
- ^ a b "Analysis: Nuclear renaissance could fizzle after Japan quake". Reuters. 2011-03-14. Archived from the original on 2015-12-08. Retrieved 2011-03-14.
- ^ "Trend in Electricity Supplied". International Atomic Energy Agency. Archived from the original on 2021-01-11. Retrieved 2021-01-09.
- ^ "Analysis: The legacy of the Fukushima nuclear disaster". Carbon Brief. 10 March 2016. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 24 March 2021.
- ^ Westall, Sylvia & Dahl, Fredrik (2011-06-24). "IAEA Head Sees Wide Support for Stricter Nuclear Plant Safety". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 2011-06-25. Retrieved 2011-06-25.
- ^ Chandler, Jo (2011-03-19). "Is this the end of the nuclear revival?". The Sydney Morning Herald. Sydney, Australia. Archived from the original on 2020-05-10. Retrieved 2020-02-20.
- ^ Belford, Aubrey (2011-03-17). "Indonesia to Continue Plans for Nuclear Power". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2020-05-10. Retrieved 2017-02-25.
- ^ Morgan, Piers (2011-03-17). "Israel Prime Minister Netanyahu: Japan situation has "caused me to reconsider" nuclear power". CNN. Archived from the original on 2019-09-30. Retrieved 2011-03-17.
- ^ "Israeli PM cancels plan to build nuclear plant". xinhuanet.com. 2011-03-18. Archived from the original on March 18, 2011. Retrieved 2011-03-17.
- ^ "Startup of Sendai Nuclear Power Unit No.1". Kyushu Electric Power Company Inc. 2015-08-11. Archived from the original on 2017-05-25. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- ^ "Japan turns back to nuclear power in post-Fukushima shift". Financial Times. London, England. 24 August 2022. Archived from the original on 30 September 2022. Retrieved November 15, 2022.
- ^ a b "Japan Is Reopening Nuclear Power Plants and Planning To Build New Ones". August 25, 2022. Archived from the original on November 15, 2022. Retrieved November 26, 2022.
- ^ "January: Taking a fresh look at the future of nuclear power". www.iea.org. Archived from the original on 2016-04-05. Retrieved 2016-04-18.
- ^ "Plans for New Reactors Worldwide". World Nuclear Association. October 2015. Archived from the original on 2016-01-31. Retrieved 2016-01-05.
- ^ "International Energy outlook 2016". US Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 15 August 2016. Retrieved 17 August 2016.
- ^ "Plans for New Nuclear Reactors Worldwide". www.world-nuclear.org. World Nuclear Association. Archived from the original on 2018-09-28. Retrieved 2018-09-29.
- ^ "Can China become a scientific superpower? – The great experiment". The Economist. 12 January 2019. Archived from the original on 25 January 2019. Retrieved 25 January 2019.
- ^ "A global nuclear phaseout or renaissance? | DW | 04.02.2021". Deutsche Welle (www.dw.com). Archived from the original on 25 November 2021. Retrieved 25 November 2021.
- ^ a b Griffiths, James. "China's gambling on a nuclear future, but is it destined to lose?". CNN. Archived from the original on 25 November 2021. Retrieved 25 November 2021.
- ^ a b "Building new nuclear plants in France uneconomical -environment agency". Reuters. 10 December 2018. Archived from the original on 25 November 2021. Retrieved 25 November 2021.
- ^ World Nuclear Association. "Nuclear Power in Japan". Archived from the original on 2020-04-01. Retrieved 2022-09-12.
- ^ "Germany's Uniper to restart coal-fired power plant as Gazprom halts supply to Europe". Reuters. 22 August 2022. Archived from the original on 2022-09-09. Retrieved 2022-09-12.
- ^ "Macron bets on nuclear in carbon-neutrality push, announces new reactors". Reuters. 10 February 2022. Archived from the original on 2022-09-14. Retrieved 2022-09-12.
- ^ "Department of Energy picks two advanced nuclear reactors for demonstration projects, announces new reactors". Science.org. 16 October 2020. Archived from the original on 24 February 2023. Retrieved 3 March 2023.
- ^ "Nuclear Power Reactors in the World – 2015 Edition" (PDF). International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 November 2020. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- ^ a b "How does a nuclear reactor make electricity?". www.world-nuclear.org. World Nuclear Association. Archived from the original on 24 August 2018. Retrieved 24 August 2018.
- ^ Spyrou, Artemis; Mittig, Wolfgang (2017-12-03). "Atomic age began 75 years ago with the first controlled nuclear chain reaction". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 2018-11-18. Retrieved 2018-11-18.
- ^ a b "Stages of the Nuclear Fuel Cycle". NRC Web. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Archived from the original on 20 April 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ a b c d "Nuclear Fuel Cycle Overview". www.world-nuclear.org. World Nuclear Association. Archived from the original on 20 April 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ "uranium Facts, information, pictures | Encyclopedia.com articles about uranium". Encyclopedia.com. 2001-09-11. Archived from the original on 2016-09-13. Retrieved 2013-06-14.
- ^ "Second Thoughts About Nuclear Power" (PDF). A Policy Brief – Challenges Facing Asia. January 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 16, 2013. Retrieved September 11, 2012.
- ^ "Uranium resources sufficient to meet projected nuclear energy requirements long into the future". Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA). 2008-06-03. Archived from the original on 2008-12-05. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
- ^ Uranium 2007 – Resources, Production and Demand. Nuclear Energy Agency, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. 2008. ISBN 978-92-64-04766-2. Archived from the original on 2009-01-30.
- ^ "Energy Supply" (PDF). p. 271. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-12-15. and table 4.10.
- ^ a b c "Waste Management in the Nuclear Fuel Cycle". Information and Issue Briefs. World Nuclear Association. 2006. Archived from the original on 2010-06-11. Retrieved 2006-11-09.
- ^ "Energy Supply" (PDF). p. 271. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-12-15. and figure 4.10.
- ^ a b c d e "Nuclear Reprocessing: Dangerous, Dirty, and Expensive". Union of Concerned Scientists. Archived from the original on 15 January 2021. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ^ a b "Toward an Assessment of Future Proliferation Risk" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 November 2021. Retrieved 25 November 2021.
- ^ a b Zhang, Hui (1 July 2015). "Plutonium reprocessing, breeder reactors, and decades of debate: A Chinese response". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. 71 (4): 18–22. doi:10.1177/0096340215590790. ISSN 0096-3402. S2CID 145763632.
- ^ a b Martin, Brian (1 January 2015). "Nuclear power and civil liberties". Faculty of Law, Humanities and the Arts – Papers (Archive): 1–6. Archived from the original on 25 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ a b Kemp, R. Scott (29 June 2016). "Environmental Detection of Clandestine Nuclear Weapon Programs". Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences. 44 (1): 17–35. Bibcode:2016AREPS..44...17K. doi:10.1146/annurev-earth-060115-012526. hdl:1721.1/105171. ISSN 0084-6597. Archived from the original on 25 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
Although commercial reprocessing involves large, expensive facilities, some of which are identifiable in structure, a small, makeshift operation using standard industrial supplies is feasible (Ferguson 1977, US GAO 1978). Such a plant could be constructed to have no visual signatures that would reveal its location by overhead imaging, could be built in several months, and once operational could produce weapon quantities of fissile material in several days
- ^ Monnet, Antoine; Gabriel, Sophie; Percebois, Jacques (1 September 2017). "Long-term availability of global uranium resources" (PDF). Resources Policy. 53: 394–407. Bibcode:2017RePol..53..394M. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2017.07.008. ISSN 0301-4207. Archived (PDF) from the original on 31 October 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
However, it can be seen that the simulation in scenario A3 stops in 2075 due to a shortage: the R/P ratio cancels itself out. The detailed calculations also show that even though it does not cancel itself out in scenario C2, the R/P ratio constantly deteriorates, falling from 130 years in 2013 to 10 years around 2100, which raises concerns of a shortage around that time. The exploration constraints thus affect the security of supply.
- ^ Haji, Maha N.; Drysdale, Jessica; Buesseler, Ken; Slocum, Alexander H. (25 June 2017). "Ocean Testing of a Symbiotic Device to Harvest Uranium From Seawater Through the Use of Shell Enclosures". Proceedings of the 27th International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference. International Society of Offshore and Polar. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021 – via OnePetro.
- ^ a b c Muellner, Nikolaus; Arnold, Nikolaus; Gufler, Klaus; Kromp, Wolfgang; Renneberg, Wolfgang; Liebert, Wolfgang (1 August 2021). "Nuclear energy - The solution to climate change?". Energy Policy. 155: 112363. Bibcode:2021EnPol.15512363M. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112363. ISSN 0301-4215. S2CID 236254316.
- ^ Chen, Yanxin; Martin, Guillaume; Chabert, Christine; Eschbach, Romain; He, Hui; Ye, Guo-an (1 March 2018). "Prospects in China for nuclear development up to 2050" (PDF). Progress in Nuclear Energy. 103: 81–90. Bibcode:2018PNuE..103...81C. doi:10.1016/j.pnucene.2017.11.011. ISSN 0149-1970. S2CID 126267852. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ Gabriel, Sophie; Baschwitz, Anne; Mathonnière, Gilles; Eleouet, Tommy; Fizaine, Florian (1 August 2013). "A critical assessment of global uranium resources, including uranium in phosphate rocks, and the possible impact of uranium shortages on nuclear power fleets". Annals of Nuclear Energy. 58: 213–220. Bibcode:2013AnNuE..58..213G. doi:10.1016/j.anucene.2013.03.010. ISSN 0306-4549.
- ^ Shang, Delei; Geissler, Bernhard; Mew, Michael; Satalkina, Liliya; Zenk, Lukas; Tulsidas, Harikrishnan; Barker, Lee; El-Yahyaoui, Adil; Hussein, Ahmed; Taha, Mohamed; Zheng, Yanhua; Wang, Menglai; Yao, Yuan; Liu, Xiaodong; Deng, Huidong; Zhong, Jun; Li, Ziying; Steiner, Gerald; Bertau, Martin; Haneklaus, Nils (1 April 2021). "Unconventional uranium in China's phosphate rock: Review and outlook". Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 140: 110740. Bibcode:2021RSERv.14010740S. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2021.110740. ISSN 1364-0321. S2CID 233577205.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Wealer, Ben; Breyer, Christian; Hennicke, Peter; Hirsch, Helmut; von Hirschhausen, Christian; Klafka, Peter; Kromp-Kolb, Helga; Präger, Fabian; Steigerwald, Björn; Traber, Thure; Baumann, Franz; Herold, Anke; Kemfert, Claudia; Kromp, Wolfgang; Liebert, Wolfgang; Müschen, Klaus (16 October 2021). "Kernenergie und Klima". Diskussionsbeiträge der Scientists for Future (in German). doi:10.5281/zenodo.5573718.
- ^ a b c d "Hidden military implications of 'building back' with new nuclear in the UK" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 October 2021. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
- ^ "USGS Scientific Investigations Report 2012–5239: Critical Analysis of World Uranium Resources". pubs.usgs.gov. Archived from the original on 19 January 2022. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ Barthel, F. H. (2007). "Thorium and unconventional uranium resources". International Atomic Energy Agency. Archived from the original on 2021-11-28. Retrieved 2021-11-28.
- ^ Dungan, K.; Butler, G.; Livens, F. R.; Warren, L. M. (1 August 2017). "Uranium from seawater – Infinite resource or improbable aspiration?". Progress in Nuclear Energy. 99: 81–85. Bibcode:2017PNuE...99...81D. doi:10.1016/j.pnucene.2017.04.016. ISSN 0149-1970.
- ^ Fang, Jianchun; Lau, Chi Keung Marco; Lu, Zhou; Wu, Wanshan (1 September 2018). "Estimating Peak uranium production in China – Based on a Stella model". Energy Policy. 120: 250–258. Bibcode:2018EnPol.120..250F. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2018.05.049. ISSN 0301-4215. S2CID 158066671.
- ^ a b Jewell, Jessica; Vetier, Marta; Garcia-Cabrera, Daniel (1 May 2019). "The international technological nuclear cooperation landscape: A new dataset and network analysis" (PDF). Energy Policy. 128: 838–852. Bibcode:2019EnPol.128..838J. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2018.12.024. ISSN 0301-4215. S2CID 159233075. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 May 2022. Retrieved 31 May 2022.
- ^ a b Xing, Wanli; Wang, Anjian; Yan, Qiang; Chen, Shan (1 December 2017). "A study of China's uranium resources security issues: Based on analysis of China's nuclear power development trend". Annals of Nuclear Energy. 110: 1156–1164. Bibcode:2017AnNuE.110.1156X. doi:10.1016/j.anucene.2017.08.019. ISSN 0306-4549.
- ^ a b Yue, Qiang; He, Jingke; Stamford, Laurence; Azapagic, Adisa (2017). "Nuclear Power in China: An Analysis of the Current and Near-Future Uranium Flows". Energy Technology. 5 (5): 681–691. doi:10.1002/ente.201600444. ISSN 2194-4296.
- ^ Ferronsky, V. I.; Polyakov, V. A. (2012). Isotopes of the Earth's Hydrosphere. Springer. p. 399. ISBN 978-94-007-2856-1.
- ^ "Toxicological profile for thorium" (PDF). Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. 1990. p. 76. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-04-22. Retrieved 2018-10-09.
world average concentration in seawater is 0.05 μg/L (Harmsen and De Haan 1980)
- ^ Huh, C. A.; Bacon, M. P. (2002). "Determination of thorium concentration in seawater by neutron activation analysis". Analytical Chemistry. 57 (11): 2138–2142. doi:10.1021/ac00288a030.
- ^ a b Seko, Noriaki (July 29, 2013). "The current state of promising research into extraction of uranium from seawater – Utilization of Japan's plentiful seas". Global Energy Policy Research. Archived from the original on October 9, 2018. Retrieved October 9, 2018.
- ^ Wang, Taiping; Khangaonkar, Tarang; Long, Wen; Gill, Gary (2014). "Development of a Kelp-Type Structure Module in a Coastal Ocean Model to Assess the Hydrodynamic Impact of Seawater Uranium Extraction Technology". Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2: 81–92. doi:10.3390/jmse2010081.
- ^ Alexandratos SD, Kung S (April 20, 2016). "Uranium in Seawater". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 55 (15): 4101–4362. doi:10.1021/acs.iecr.6b01293.
- ^ a b c d Finck, Philip. "Current Options for the Nuclear Fuel Cycle" (PDF). JAIF. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-12.
- ^ a b "Backgrounder on Radioactive Waste". NRC. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Archived from the original on 13 November 2017. Retrieved 20 April 2021.
- ^ "A fast reactor system to shorten the lifetime of long-lived fission products".
- ^ "Radioactivity: Minor Actinides". www.radioactivity.eu.com. Archived from the original on 2018-12-11. Retrieved 2018-12-23.
- ^ Ojovan, Michael I. (2014). An introduction to nuclear waste immobilisation, second edition (2nd ed.). Kidlington, Oxford, U.K.: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-08-099392-8.
- ^ "High-level radioactive waste". nuclearsafety.gc.ca. Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission. February 3, 2014. Archived from the original on April 14, 2022. Retrieved April 19, 2022.
- ^ Hedin, A. (1997). Spent nuclear fuel - how dangerous is it? A report from the project 'Description of risk' (Technical report). Energy Technology Data Exchange.
- ^ Bruno, Jordi; Duro, Laura; Diaz-Maurin, François (2020). "Chapter 13 – Spent nuclear fuel and disposal". Advances in Nuclear Fuel Chemistry. Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy. Woodhead Publishing. pp. 527–553. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-102571-0.00014-8. ISBN 978-0-08-102571-0. S2CID 216544356. Archived from the original on 2021-09-20. Retrieved 2021-09-20.
- ^ Ojovan, M. I.; Lee, W. E. (2005). An Introduction to Nuclear Waste Immobilisation. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier Science Publishers. p. 315. ISBN 978-0-08-044462-8.
- ^ National Research Council (1995). Technical Bases for Yucca Mountain Standards. Washington, DC: National Academy Press. p. 91. ISBN 978-0-309-05289-4.
- ^ "The Status of Nuclear Waste Disposal". The American Physical Society. January 2006. Archived from the original on 2008-05-16. Retrieved 2008-06-06.
- ^ "Public Health and Environmental Radiation Protection Standards for Yucca Mountain, Nevada; Proposed Rule" (PDF). United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2005-08-22. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2008-06-26. Retrieved 2008-06-06.
- ^ "CRS Report for Congress. Radioactive Waste Streams: Waste Classification for Disposal" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-08-29. Retrieved 2018-12-22.
The Nuclear Waste Policy Act of 1982 (NWPA) defined irradiated fuel as spent nuclear fuel, and the byproducts as high-level waste.
- ^ Vandenbosch 2007, p. 21.
- ^ Clark, Duncan (2012-07-09). "Nuclear waste-burning reactor moves a step closer to reality | Environment | guardian.co.uk". Guardian. London, England. Archived from the original on 2022-10-08. Retrieved 2013-06-14.
- ^ Monbiot, George (5 December 2011). "A Waste of Waste". Monbiot.com. Archived from the original on 2013-06-01. Retrieved 2013-06-14.
- ^ "Energy From Thorium: A Nuclear Waste Burning Liquid Salt Thorium Reactor". YouTube. 2009-07-23. Archived from the original on 2021-12-11. Retrieved 2013-06-14.
- ^ "Role of Thorium to Supplement Fuel Cycles of Future Nuclear Energy Systems" (PDF). IAEA. 2012. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 7 April 2021.
Once irradiated in a reactor, the fuel of a thorium–uranium cycle contains an admixture of 232U (half-life 68.9 years) whose radioactive decay chain includes emitters (particularly 208Tl) of high energy gamma radiation (2.6 MeV). This makes spent thorium fuel treatment more difficult, requires remote handling/control during reprocessing and during further fuel fabrication, but on the other hand, may be considered as an additional non-proliferation barrier.
- ^ "NRC: Low-Level Waste". www.nrc.gov. Archived from the original on 17 August 2018. Retrieved 28 August 2018.
- ^ "The Challenges of Nuclear Power". Archived from the original on 2017-05-10. Retrieved 2013-01-04.
- ^ "Coal Ash Is More Radioactive than Nuclear Waste". Scientific American. 2007-12-13. Archived from the original on 2013-06-12. Retrieved 2012-09-11.
- ^ Gabbard, Alex (2008-02-05). "Coal Combustion: Nuclear Resource or Danger". Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Archived from the original on February 5, 2007. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ "Coal ash is not more radioactive than nuclear waste". CE Journal. 2008-12-31. Archived from the original on 2009-08-27.
- ^ "Yankee Nuclear Power Plant". Yankeerowe.com. Archived from the original on 2006-03-03. Retrieved 2013-06-22.
- ^ "Why nuclear energy". Generation Atomic. 26 January 2021. Archived from the original on 23 December 2018. Retrieved 22 December 2018.
- ^ "NPR Nuclear Waste May Get A Second Life". NPR. Archived from the original on 2018-12-23. Retrieved 2018-12-22.
- ^ "Energy Consumption of the United States - The Physics Factbook". hypertextbook.com. Archived from the original on 2018-12-23. Retrieved 2018-12-22.
- ^ "NRC: Dry Cask Storage". Nrc.gov. 2013-03-26. Archived from the original on 2013-06-02. Retrieved 2013-06-22.
- ^ a b Montgomery, Scott L. (2010). The Powers That Be, University of Chicago Press, p. 137.
- ^ "international Journal of Environmental Studies, The Solutions for Nuclear waste, December 2005" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-04-26. Retrieved 2013-06-22.
- ^ "Oklo: Natural Nuclear Reactors". U.S. Department of Energy Office of Civilian Radioactive Waste Management, Yucca Mountain Project, DOE/YMP-0010. November 2004. Archived from the original on 2009-08-25. Retrieved 2009-09-15.
- ^ a b Gore, Al (2009). Our Choice: A Plan to Solve the Climate Crisis. Emmaus, Pennsylvania: Rodale. pp. 165–166. ISBN 978-1-59486-734-7.
- ^ Muller, Richard A.; Finsterle, Stefan; Grimsich, John; Baltzer, Rod; Muller, Elizabeth A.; Rector, James W.; Payer, Joe; Apps, John (May 29, 2019). "Disposal of High-Level Nuclear Waste in Deep Horizontal Drillholes". Energies. 12 (11): 2052. doi:10.3390/en12112052.
- ^ Mallants, Dirk; Travis, Karl; Chapman, Neil; Brady, Patrick V.; Griffiths, Hefin (February 14, 2020). "The State of the Science and Technology in Deep Borehole Disposal of Nuclear Waste". Energies. 13 (4): 833. doi:10.3390/en13040833.
- ^ "A Nuclear Power Renaissance?". Scientific American. 2008-04-28. Archived from the original on 2017-05-25. Retrieved 2008-05-15.
- ^ von Hippel, Frank N. (April 2008). "Nuclear Fuel Recycling: More Trouble Than It's Worth". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 2008-11-19. Retrieved 2008-05-15.
- ^ "Licence granted for Finnish used fuel repository". World Nuclear News. 2015-11-12. Archived from the original on 2015-11-24. Retrieved 2018-11-18.
- ^ Poinssot, Ch.; Bourg, S.; Ouvrier, N.; Combernoux, N.; Rostaing, C.; Vargas-Gonzalez, M.; Bruno, J. (May 2014). "Assessment of the environmental footprint of nuclear energy systems. Comparison between closed and open fuel cycles". Energy. 69: 199–211. Bibcode:2014Ene....69..199P. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2014.02.069.
- ^ a b c R. Stephen Berry and George S. Tolley, Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing Archived 2017-05-25 at the Wayback Machine, The University of Chicago, 2013.
- ^ Fairley, Peter (February 2007). "Nuclear Wasteland". IEEE Spectrum. Archived from the original on 2020-08-05. Retrieved 2020-02-02.
- ^ a b "Processing of Used Nuclear Fuel". World Nuclear Association. 2018. Archived from the original on 2018-12-25. Retrieved 2018-12-26.
- ^ Campbell, D. O.; Gift, E. H. (1978). Proliferation-resistant nuclear fuel cycles. [Spiking of plutonium with /sup 238/Pu] (Technical report). Oak Ridge National Laboratory. doi:10.2172/6743129. OSTI 6743129 – via Office of Scientific and Technical Information.
- ^ Fedorov, M. I.; Dyachenko, A. I.; Balagurov, N. A.; Artisyuk, V. V. (2015). "Formation of proliferation-resistant nuclear fuel supplies based on reprocessed uranium for Russian nuclear technologies recipient countries". Nuclear Energy and Technology. 1 (2): 111–116. Bibcode:2015NEneT...1..111F. doi:10.1016/j.nucet.2015.11.023.
- ^ Lloyd, Cody; Goddard, Braden (2018). "Proliferation resistant plutonium: An updated analysis". Nuclear Engineering and Design. 330: 297–302. Bibcode:2018NuEnD.330..297L. doi:10.1016/j.nucengdes.2018.02.012.
- ^ a b Feiveson, Harold; et al. (2011). "Managing nuclear spent fuel: Policy lessons from a 10-country study". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. Archived from the original on 2012-04-26. Retrieved 2016-07-18.
- ^ Kok, Kenneth D. (2010). Nuclear Engineering Handbook. CRC Press. p. 332. ISBN 978-1-4200-5391-3.
- ^ Jarry, Emmanuel (6 May 2015). "Crisis for Areva's plant as clients shun nuclear". Moneyweb. Reuters. Archived from the original on 23 July 2015. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- ^ David, S. (2005). "Future Scenarios for Fission Based Reactors". Nuclear Physics A. 751: 429–441. Bibcode:2005NuPhA.751..429D. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2005.02.014.
- ^ Brundtland, Gro Harlem (20 March 1987). "Chapter 7: Energy: Choices for Environment and Development". Our Common Future: Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development. Oslo. Archived from the original on 21 January 2013. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
Today's primary sources of energy are mainly non-renewable: natural gas, oil, coal, peat, and conventional nuclear power. There are also renewable sources, including wood, plants, dung, falling water, geothermal sources, solar, tidal, wind, and wave energy, as well as human and animal muscle-power. Nuclear reactors that produce their own fuel ('breeders') and eventually fusion reactors are also in this category
- ^ John McCarthy (2006). "Facts From Cohen and Others". Progress and its Sustainability. Stanford. Archived from the original on 2007-04-10. Retrieved 2006-11-09. Citing: Cohen, Bernard L. (January 1983). "Breeder reactors: A renewable energy source". American Journal of Physics. 51 (1): 75–76. Bibcode:1983AmJPh..51...75C. doi:10.1119/1.13440. S2CID 119587950.
- ^ "Advanced Nuclear Power Reactors". Information and Issue Briefs. World Nuclear Association. 2006. Archived from the original on 2010-06-15. Retrieved 2006-11-09.
- ^ "Synergy between Fast Reactors and Thermal Breeders for Safe, Clean, and Sustainable Nuclear Power" (PDF). World Energy Council. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-01-10. Retrieved 2013-02-03.
- ^ Kessler, Rebecca. "Are Fast-Breeder Reactors A Nuclear Power Panacea? by Fred Pearce: Yale Environment 360". E360.yale.edu. Archived from the original on 2013-06-05. Retrieved 2013-06-14.
- ^ a b "Fast Neutron Reactors | FBR – World Nuclear Association". www.world-nuclear.org. Archived from the original on 23 December 2017. Retrieved 7 October 2018.
- ^ "Prototype fast breeder reactor to be commissioned in two months: IGCAR director". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 15 September 2018. Retrieved 28 August 2018.
- ^ "India's breeder reactor to be commissioned in 2013".


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch


