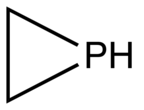
Phosphirane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Phosphirane | |
| Systematic IUPAC name Phosphacyclopropane | |
| Other names Phosphiran | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H5P | |
| Molar mass | 60.036 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless gas |
| Melting point | −121 °C (−186 °F; 152 K) |
| Boiling point | 36.5 °C (97.7 °F; 309.6 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Phosphirane is the organophosphorus compound with the formula C2H4PH. It is a colorless gas of no commercial value. As the simplest cyclic, saturated organophosphorus compound, phosphirane is the prototype of a family of related compounds that have attracted attention from the research community. Phosphirane was first prepared by reaction of 1,2-dichloroethane with the conjugate base of phosphine.[2] Phosphiranes, that is substituted phosphirene compounds where one or more of the H's are replaced organic substituents, are far more commonly discussed than the parent phosphirane.
References
[edit]- ^ Wagner, Ross I.; Freeman, LeVern D.; Goldwhite, H.; Rowsell, D. G. (March 1967). "Phosphiran". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 89 (5): 1102–1104. doi:10.1021/ja00981a013.
- ^ François Mathey; Manfred Regitz (1996). "Phosphiranes, Phosphirenes, and Heavier Analogues". Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry II. Vol. 1A. pp. 277–304. doi:10.1016/B978-008096518-5.00008-3. ISBN 978-0-08-096518-5.
- Quin, L. D. (2000). A Guide to Organophosphorus Chemistry. Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 0-471-31824-8.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch