Saharat Thai Doem
| Saharat Thai Doem สหรัฐไทยเดิม | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subdivision of Thailand | |||||||||
| 1943–1945 | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Anthem | |||||||||
| Phleng Chat Thai | |||||||||
| Capital | Kengtung | ||||||||
| Historical era | World War II | ||||||||
| 18 August 1943 | |||||||||
• Thailand returns annexed territories to the United Kingdom | 15 August 1945 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Myanmar | ||||||||
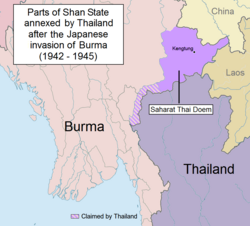
Saharat Thai Doem (Thai: สหรัฐไทยเดิม, lit. 'Unified Former Thai Territories') was an administrative division of Thailand. It encompassed parts of the Shan States of British Burma annexed by the Thai government after the Japanese conquest of Burma.
By means of this annexation, Axis-aligned Thailand expanded northwards to the 22nd parallel north and gained a border with China. Chiang Tung (Kengtung) was the administrative headquarters of the province.[1] After the Phibun government fell in August 1944, the new Thai government communicated to the British that it renounced all claims to the Shan States and northern Malaya, and that it would immediately return the territories to Britain. The Churchill government did not accept the Thai overture, and was prepared to retaliate.[2] The Thai army evacuated in August 1945.[3]
Geography
[edit]
The territory of the Northern Thai province was mountainous, except for a few small areas, such as the intermontane basin of Kengtung. The Salween River marked the western border of the new province. The northernmost point was the frontier town of Pangsang.
There were few roads connecting the districts and most of the population lived in small mountain villages. The area was mostly inhabited by Tai Yai people, but there were also sizable communities of Lahu, Akha and Wa people, as well as those belonging to the Karen ethnic group, including the Red Karen and the Kayan people.
History
[edit]

Thai Prime Minister Plaek Phibunsongkhram signed a secret agreement with the Japanese Empire on 14 December 1941 and committed the Thai armed forces to participate in the planned Malayan Campaign and Burma Campaign. An alliance between Thailand and Japan was signed on 21 December 1941. On 25 January 1942, the Thai government, believing the Allies beaten, declared war on the United States and the United Kingdom. As a reward for entering into a military alliance with them, the Japanese agreed to return to Thailand Kedah, Perlis, Kelantan, and Terengganu, the four Malayan provinces ceded to the British in 1909, as well as parts of Shan State in British Burma that were deemed "lost territories" of Thailand.[4][5]
In accordance with the Thai military alliance with Japan that was signed on 21 December 1941, the Japanese agreed that the area of eastern Shan State east of the Salween was to be under Thai administration.
In 1942, the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) accompanied by the Thai Phayap Army invaded the Federated Shan States from Thailand. The defense of the Shan States had been left to the Nationalist Chinese forces, upon the request of the British. The 93rd Division of the Chinese Army defended Kengtung, while the 249th and 55th Divisions guarded from the Kengtung to Karenni States along the Thai border. The Japanese forces with superior air power went on to dislodge the Nationalist Chinese forces by November 1942.[6] The IJA allowed the Phayap Army to occupy all of Kengtung State and the four trans-Salween districts of Möng Tang, Möng Hang, Möng Kyawt and Möng Hta, of Mongpan State. Following the existing agreement between Thai Prime Minister Plaek Phibunsongkhram (Phibun) and the Japanese Empire, on 18 August 1943, the Japanese government agreed to the Thai annexation of Kengtung and part of Mongpan State (as well as the annexation of Kelantan, Trengganu, Kedah, Perlis states and nearby islands in Malaya.)[7] The Thai government wanted the two districts of Möngmaü and Mehsakun of Mawkmai of the southern Shan states as well as part of Kantarawadi in the Karenni states, all east of the Salween River, but the Japanese assigned them to their client State of Burma in September 1943.[8]
Panglong, a Chinese Muslim town in British Burma, was entirely destroyed by the Japanese invaders in the Japanese invasion of Burma.[9] The Hui Muslim Ma Guanggui became the leader of the Hui Panglong self defense guard created by Su who was sent by the Kuomintang government of the Republic of China to fight against the Japanese invasion of Panglong in 1942. The Japanese destroyed Panglong, burning it and driving out the over 200 Hui households out as refugees. Yunnan and Kokang received Hui refugees from Panglong driven out by the Japanese. One of Ma Guanggui's nephews was Ma Yeye, a son of Ma Guanghua and he narrated the history of Panglang included the Japanese attack.[10] An account of the Japanese attack on the Hui in Panglong was written and published in 1998 by a Hui from Panglong called "Panglong Booklet".[11] The Japanese attack in Burma caused the Hui Mu family to seek refuge in Panglong but they were driven out again to Yunnan from Panglong when the Japanese attacked Panglong.[12]
The Thai army would remain there until the end of the war although the Thai government began to alter its position when the tide of war began to favor the allies. After the Phibun government fell in August 1944, the new government of Khuang Aphaiwong communicated to the British government it renounced all claims to the Shan States and northern Malaya, and that it would immediately return the territories to Britain. The Churchill government did not accept the Thai overture, and was prepared to retaliate.[2] The Thai army evacuated the two Shan States only in August 1945.[3]
Administration
[edit]
A rudimentary administration was set up early in the invasion with Kengtung as the centre. Made up mostly of small rural communities, during the occupation the Thai territory in Shan State remained a largely forgotten place. Wounded or ill Thai soldiers who were sent to Bangkok were shocked that there was no knowledge or concern about the hardships of the northern Thai Army in the newly annexed territory.[13]
Authorities
[edit]Thai Military governor in Kengtung and Möngpan
[edit]- Dec 1942–1945 Phin Choonhavan (b. 1891 – d. 1973)
Administrative divisions
[edit]
Saharat Thai Doem was divided into twelve districts (amphoe), to which later a further district was added. Mueang Phan was a special district.[14]
| Name | Thai | corresponding to Burmese | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mueang Chiang Tung | เมืองเชียงตุง | Kengtung District |
| 2 | Mueang Yong | เมืองยอง | Mong Yawng Township |
| 3 | Mueang Phayak | เมืองพยาค | Mong Hpayak District |
| 4 | Mueang Yu | เมืองยู้ | |
| 5 | Mueang Ching | เมืองชิง | |
| 6 | Mueang Ma | เมืองมะ | |
| 7 | Mueang Yang | เมืองยาง | Mong Yang Township |
| 8 | Mueang Khak | เมืองขาก | |
| 9 | Mueang Len | เมืองเลน | |
| 10 | Mueang Ko | เมืองโก | |
| 11 | Mueang Sat | เมืองสาด | Mong Hsat Township |
| 12 | Mueang Hang | เมืองหาง | Mong Hang Village, Mong Tong Township |
| – | Mueang Phan* | เมืองพาน | The four districts of Möng Tang, Möng Hang, Möng Kyawt and Möng Hta belonging to Mong Pan Township |
Historical events
[edit]- The Thai flag was hoisted in Kengtung on 5 June 1942. Kengtung (Chiang Tung) would become the capital city of the new Thai province.
- The Thai military reached as far as Mandalay, but the Japanese only sanctioned the annexation of part of the territories conquered. Thai tanks took part in the battles near Taunggyi.
- Thai and Japanese soldiers met in Mandalay (Burma Campaign 1942).
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Ronald Bruce St. John, The Land Boundaries of Indochina: Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam, p. 20
- ^ a b Aung Tun 2009: 205
- ^ a b Seekins 2006: 251
- ^ "A Forgotten Invasion: Thailand in Shan State, 1941–45"
- ^ "สงครามมหาเอเซียบูรพา – จากวันวีรไทย ถึง วันประกาศสงคราม". Samphan. I See History dot com. September 2009. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 8 August 2010.
- ^ Aung Tun 2009: 195–196
- ^ Aung Tun 2009: 202
- ^ Aung Tun 2009: 203–204, 205–206
- ^ Forbes, Andrew; Henley, David (December 2015). "'Saharat Tai Doem' Thailand in Shan State, 1941–45". CPA Media.
- ^ Wen-Chin Chang (16 January 2015). Beyond Borders: Stories of Yunnanese Chinese Migrants of Burma. Cornell University Press. pp. 122–. ISBN 978-0-8014-5450-9.
- ^ Wen-Chin Chang (16 January 2015). Beyond Borders: Stories of Yunnanese Chinese Migrants of Burma. Cornell University Press. pp. 124–. ISBN 978-0-8014-5450-9.
- ^ Wen-Chin Chang (16 January 2015). Beyond Borders: Stories of Yunnanese Chinese Migrants of Burma. Cornell University Press. pp. 129–. ISBN 978-0-8014-5450-9.
- ^ Bangkok Post – A Forgotten Invasion: Thailand in Shan State, 1941–45 by Andrew Forbes in Axis History Forum
- ^ "ประกาสกองบันชาการทหานสูงสุด เรื่องการปกครองสหรัถไทยเดิม" (PDF). ราชกิจจานุเบกสา (in Thai). 60 (31ก): 1082–1083. 15 June 1943. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 November 2011.
Bibliography
[edit]- Aung Tun, Sai (2009). History of the Shan State: From Its Origins to 1962. Chiang Mai: Silk Worm Books. ISBN 978-974-9511-43-5.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch
