Tau4 Eridani
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Eridanus |
| Right ascension | 03h 19m 31.0006s [1] |
| Declination | −21° 45′ 28.315″ [1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.65[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | asymptotic giant branch[3] |
| Spectral type | M3/4 III[4] |
| U−B color index | +1.79[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.61[2] |
| Variable type | Lb[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +41.7±0.7[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +52.774 mas/yr[1] Dec.: +32.718 mas/yr[1] |
| Parallax (π) | 10.6153 ± 0.3213 mas[1] |
| Distance | 307 ± 9 ly (94 ± 3 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.79[7] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.73±0.3[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 103[9] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,537[10] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.91[11] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,652[9] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Tau4 Eridani (τ4 Eridani, τ4 Eri) is a binary star system in the constellation Eridanus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.65.[2] The distance to this star can be estimated using the parallax method, which yields a value of roughly 300 light years. [1]
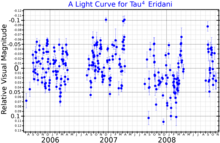
This is an evolved red giant star currently on the asymptotic giant branch[3] with a stellar classification of M3/4 III.[4] It is a slow irregular variable star of type Lb, undergoing changes in magnitude over the range 3.57−3.72[5] with a periodicity of 23.8 d.[13] The measured angular diameter of Tau4 Eridani is 10.58±1.00 mas.[14] At its estimated distance, this yields a physical size of about 106 times the radius of the Sun.[15] It shines with 1,537[10] times the luminosity of the Sun from an outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 3,650 K.[9]
This is most likely a binary star system.[16] The companion is a magnitude 9.5 star at an angular separation of 5.7″ along a position angle of 291°, as of 2013.[17]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b c d Mermilliod, J.-C. (1986), "Compilation of Eggen's UBV data, transformed to UBV (unpublished)", Catalogue of Eggen's UBV Data, SIMBAD, Bibcode:1986EgUBV........0M.
- ^ a b Lebzelter, T.; Hron, J. (January 2008), "BRITE stars on the AGB" (PDF), Communications in Asteroseismology, 152: 178–181, Bibcode:2008CoAst.152..178L, doi:10.1553/cia152s178.
- ^ a b Houk, N.; Smith-Moore, M. (1988), Michigan Catalogue of Two-dimensional Spectral Types for the HD Stars, vol. 4, Bibcode:1988mcts.book.....H.
- ^ a b Ruban, E. V.; et al. (September 2006), "Spectrophotometric observations of variable stars", Astronomy Letters, 32 (9): 604–607, Bibcode:2006AstL...32..604R, doi:10.1134/S1063773706090052, S2CID 121747360.
- ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006), "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system", Astronomy Letters, 32 (11): 759–771, arXiv:1606.08053, Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G, doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065, S2CID 119231169.
- ^ Cardini, D. (January 2005), "Mg II chromospheric radiative loss rates in cool active and quiet stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 430: 303–311, arXiv:astro-ph/0409683, Bibcode:2005A&A...430..303C, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041440, S2CID 12136256.
- ^ Halabi, Ghina M.; Eid, Mounib El (2015). "Exploring masses and CNO surface abundances of red giant stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 451 (3): 2957. arXiv:1507.01517. Bibcode:2015MNRAS.451.2957H. doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1141. S2CID 118707332.
- ^ a b c Wood, Brian E.; Müller, Hans-Reinhard; Harper, Graham M. (2016-09-23), "Hubble Space Telescope Constraints on the Winds and Astrospheres of Red Giant Stars", The Astrophysical Journal, 829 (2): 74, arXiv:1607.07732, Bibcode:2016ApJ...829...74W, doi:10.3847/0004-637X/829/2/74, ISSN 0004-637X
- ^ a b McDonald, I.; et al. (2012), "Fundamental Parameters and Infrared Excesses of Hipparcos Stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 427 (1): 343–57, arXiv:1208.2037, Bibcode:2012MNRAS.427..343M, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x, S2CID 118665352.
- ^ Ayres, Thomas (2023-05-01), "In the Trenches of the Solar-Stellar Connection. VII. Wilson-Bappu 2022", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 266 (1): 6, Bibcode:2023ApJS..266....6A, doi:10.3847/1538-4365/acb535, ISSN 0067-0049 Tau4 Eridani database entry at VizieR.
- ^ "tau04 Eri". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2016-10-13.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ a b Tabur, V.; et al. (December 2009), "Long-term photometry and periods for 261 nearby pulsating M giants", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 400 (4): 1945–1961, arXiv:0908.3228, Bibcode:2009MNRAS.400.1945T, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15588.x, S2CID 15358380.
- ^ Richichi, A.; Percheron, I. (May 2005), "First results from the ESO VLTI calibrators program", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 434 (3): 1201–1209, arXiv:astro-ph/0501532, Bibcode:2005A&A...434.1201R, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20042257, S2CID 2847613.
- ^ Lang, Kenneth R. (2006), Astrophysical formulae, Astronomy and astrophysics library, vol. 1 (3 ed.), Birkhäuser, ISBN 3-540-29692-1. The radius (R*) is given by:
- ^ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 389 (2): 869–879, arXiv:0806.2878, Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x, S2CID 14878976.
- ^ Mason, B. D.; et al. (2014), "The Washington Visual Double Star Catalog", The Astronomical Journal, 122 (6): 3466–3471, Bibcode:2001AJ....122.3466M, doi:10.1086/323920, retrieved 2015-07-22


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch
