Urogenital triangle
| Urogenital triangle | |
|---|---|
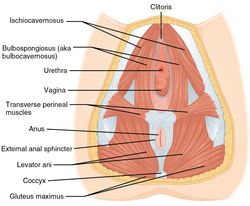 Muscles of the female perineum. (Urogenital triangle is roughly equal to top half of diagram.) | |
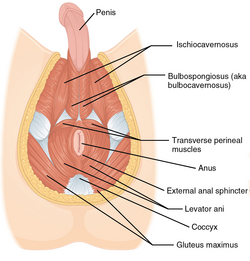 Muscles of male perineum. (Urogenital triangle is roughly equal to top half of diagram.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | regio urogenitalis |
| TA98 | A01.2.06.003 |
| TA2 | 279 |
| FMA | 20348 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The urogenital triangle is the anterior part of the perineum. In female mammals, it contains the vulva, while in male mammals, it contains the penis and scrotum.
Structure
[edit]The urogenital triangle is the area bound by a triangle with one vertex at the pubic symphysis and the two other vertices at the iliac tuberosities of the pelvic bone.
Components
[edit]As might be expected, the contents of the urogenital triangle differ greatly between the male and the female. Some of the components include:[1]
- Posterior scrotal nerves / posterior labial nerves
- Urethra
- Vagina
- Bulbourethral gland / Bartholin's gland
- Muscles
- Penile crura / clitoral crura
- Bulb of penis / vestibular bulbs
- Urogenital diaphragm
- Muscular perineal body
- Superficial and deep perineal pouch
- Blood vessels and lymphatics
Additional images
[edit]- Articulations of pelvis. Anterior view.
- The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery.
- The posterior aspect of the rectum exposed by removing the lower part of the sacrum and the coccyx.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. ISBN 9788131225561.
External links
[edit]- Anatomy photo:41:01-0201 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Perineum: Boundaries of the Female Perineum"
- perineum at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (perineumboundaries)


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch