3,3',5'-Triiodothyronine — Wikipédia
| 3,3',5'-Triiodothyronine | |
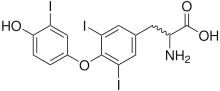
 Structure de la 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | acide (2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophénoxy)-3-iodophényl]propanoïque |
| Synonymes | triiodothyronine inverse, |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 644280 |
| ChEBI | 28774 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C15H12I3NO4 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 650,973 5 ± 0,014 3 g/mol C 27,68 %, H 1,86 %, I 58,48 %, N 2,15 %, O 9,83 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
| modifier | |
La 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine, ou triiodothyronine inverse (rT3), est un métabolite issu de la désiodation de la thyroxine. C'est un isomère biologiquement inactif de l'hormone thyroïdienne T3, ou 3,3',5-triiodothyronine.
Notes et références
[modifier | modifier le code]- ↑ Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch