Guibourtinidol — Wikipédia
| guibourtinidol | |
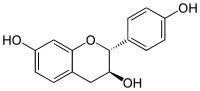 | |
| Structure du guibourtinidol. | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Synonymes | Leucoguibourtinidine |
| PubChem | 9878329 |
| SMILES | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C15H14O4 |
| Masse molaire[1] | 258,269 3 ± 0,014 2 g/mol C 69,76 %, H 5,46 %, O 24,78 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
| modifier | |
Le guibourtinidol est un flavan-3-ol.
Les proguibourtinidines sont un type de tanins condensés. Les tanins condensés sont des polymères de flavanols et les proguibourtinidines sont notamment composées d'unités de guibourtinidol. Le nom provient du fait que ces tanins produisent de la guibourtinidine, une anthocyanidine, lors de leur hydrolyse en milieu acide.
Références
[modifier | modifier le code]- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Reinier J.J. Nel, Makhosazana Mthembu, Johan Coetzee, Hendrik van Rensburg, Elfranco Malan and Daneel Ferreira, 1999. The novel Flavan-3-ol, (2R,3S )-guibourtinidol and its diastereomers. Phytochemistry 52, pages 1153-1158.
- (en) Jan P. Steynberg, Daneel Ferreira and David G. Roux, 1987. Synthesis of condensed tannins. Part 18. Stilbenes as potent nucleophiles in regio- and stereo-specific condensations: novel guibourtinidol-stilbenes from Guibourtia coleosperma.
- (en) Elfranco Malan, Ewald Swinny, Daneel Ferreira and Petrus Steynberg, 1996. The structure and synthesis of proguibourtinidins from Cassia abbreviata.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch