塩化イットリウム(III)
| 塩化イットリウム(III) | |
|---|---|
 | |
Yttrium(III) chloride | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 10361-92-9 |
| ChemSpider | 59696 |
| RTECS番号 | ZG3150000 |
| |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | YCl3 |
| モル質量 | 195.26 g/mol |
| 外観 | 白色固体 |
| 密度 | 2.67 g/cm3 |
| 融点 | 721 °C, 994 K, 1330 °F |
| 沸点 | 1507 °C, 1780 K, 2745 °F ([2]) |
| 水への溶解度 | 82 g/100 mL |
| 溶解度 | 60.1 g/100 mL エタノール (15 °C) 60.6 g/100 mL ピリジン (15°C)[1] |
| 構造 | |
| 結晶構造 | 単斜晶, mS16 |
| 空間群 | C12/m1, No. 12 |
| 危険性 | |
| EU Index | Not listed |
| 引火点 | 不燃性 |
| 関連する物質 | |
| その他の陰イオン | フッ化イットリウム(III) 臭化イットリウム(III) ヨウ化イットリウム(III) |
| その他の陽イオン | 塩化スカンジウム(III) 塩化ランタン(III) 塩化アクチニウム(III) |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
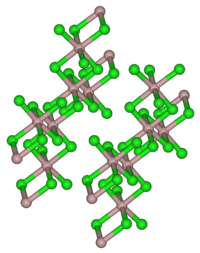
塩化イットリウム(III)(えんかイットリウム さん、英: yttrium(III) chloride)はイットリウムの塩化物で、組成式は YCl3 である。室温では固体の塩であり、水によく溶ける潮解性の物質である。固体のYCl3は、YCl6八面体が隣の八面体と3つの角を共有する結果、層状構造を成している[3]。この構造は三塩化アルミニウムに代表される一連の化合物で共通のものである。
YCl3 は触媒として使われたり、超伝導体内に使われる。また、肺水腫や肝臓病と関係がある[2][4]。
反応
[編集]塩化イットリウム(III)は塩酸と酸化イットリウム(III)の反応で得られる[5]。また、他の方法でも得られる[1]。
分解は、
出典
[編集]- ^ a b Spencer, James F. (1919), The Metals of the Rare Earths, New York: Longmans, Green, and Co, pp. 135 2008年5月29日閲覧。
- ^ a b Yttrium & Compounds, United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration, (2007-01-11), オリジナルの2013年3月2日時点におけるアーカイブ。 2008年5月29日閲覧。
- ^ Wells A.F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry 5th edition Oxford Science Publications ISBN 0-19-855370-6
- ^ Gangolli, S. (1999), The Dictionary of Substances and Their Effects, London: Royal Society of Chemistry, pp. 666–7, ISBN 9780854048380 2008年5月29日閲覧。
- ^ Turner, Jr., Francis M.; Berolzheimer, Daniel D.; Cutter, William P.; Helfrich, John (1920), The Condensed Chemical Dictionary, New York: Chemical Catalog Company, pp. 492 2008年5月29日閲覧。


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch![{\displaystyle {\ce {10NH4Cl + Y2O3 -> 2(NH4)2[YCl5] + 6NH3 + 3H2O}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8659d9d449ec62f1931e1b12be274946448814ca)
![{\displaystyle {\ce {YCl3\cdot {6H2O}+2NH4Cl->{(NH4)2[YCl5]}+6H2O}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/269d0fd51151ebc8432a11bbfd1c29c36ffb111f)
![{\displaystyle {\ce {{(NH4)2[YCl5]}-> {2NH4Cl}+ YCl3}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fdf0049f91c5cbdefbe33c75ae2d550d87da27ac)