臭化インジウム(I)
| 臭化インジウム(I) | |
|---|---|
 | |
Indium(I) bromide | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 14280-53-6 |
| PubChem | 71317298 |
| ChemSpider | 21106449 |
| |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | InBr |
| モル質量 | 194.722 g/mol |
| 密度 | 4.960 g/cm3 |
| 融点 | 285 °C, 558 K, 545 °F |
| 沸点 | 656 °C, 929 K, 1213 °F |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
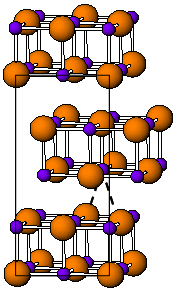
臭化インジウム(I)(Indium(I) bromide)は、インジウムと臭素からなる化合物である。赤色の結晶で、ヨウ化タリウム(I)と同じ歪んだ岩塩型構造を持つ[1]。通常、金属インジウムを臭化インジウム(III)とともに加熱することで合成する。硫黄ランプに用いられる。有機化学では、α, α-のジクロロケトンのカップリングで1-アリル-ブタン-1,4-ジオンを合成する反応を促進する[2]。例えば、ハロゲン化アルキルからハロゲン化アルキルインジウムを得たり[3]、臭化ニッケル錯体からニッケル-インジウム結合を得る[4]酸化付加反応が知られている。水中では不安定で、金属インジウムと臭化インジウム(III)に分解する。臭化インジウム(II)を水に溶解すると、赤い沈殿として臭化インジウム(I)が生成し、急速に分解する[5]。
関連項目
[編集]出典
[編集]- ^ Stephenson N.C., Mellor D.P. "The crystal structure of indium monobromide" Australian journal of scientific research A 3 (1950) 581-586
- ^ C. Peppe and R. Pavão das Chagas (2004). “Indium(I) Bromide-Mediated Reductive Coupling of α,α-Dichloroketones to 1-Aryl-butane-1,4-diones”. Synlett (7): 1187–1190. doi:10.1055/s-2004-825591.
- ^ M. J. S. Gynane, L. G. Waterworth and I. J. Worrall (1972). “Oxidative addition reactions of group III metals in low oxidation states III. Reactions of indium monohalides with alkyl halides”. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 43 (2): 257–264. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)81599-5.
- ^ J. Weiss, T. Priermeier and R. A. Fischer (1996). “Reactions of Elemental Indium and Indium(I) Bromide with Nickel-Bromine Bonds: Structure of (η5-C5H5)(Ph3P)Ni-InBr2(O=PPh3)”. Inorg. Chem. 35 (1): 71–75. doi:10.1021/ic950614i. PMID 11666166.
- ^ R. Dronskowski (1994). “Ambient-Temperature Formation of Crystalline Indium Monohalides from Aqueous Media”. Inorg. Chem. 33 (25): 5960–5963. doi:10.1021/ic00103a054.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch