Acetic acid - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| |||
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Acetic acid[3] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name Ethanoic acid | |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| 3DMet | |||
| Abbreviations | AcOH | ||
| Beilstein Reference | 506007 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.528 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E260 (preservatives) | ||
| Gmelin Reference | 1380 | ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Acetic+acid | ||
PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2789 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 60.05 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Odor | Pungent/Vinegar-like | ||
| Density | 1.049 g cm−3 (liquid); 1.27 g cm cm−3 (solid) | ||
| Melting point | 16 to 17 °C; 61 to 62 °F; 289 to 290 K | ||
| Boiling point | 118 to 119 °C; 244 to 246 °F; 391 to 392 K | ||
| Miscible | |||
| log P | -0.28[4] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | |||
| Basicity (pKb) | 9.24 (basicity of acetate ion) | ||
| Conjugate base | Acetate | ||
| -31.54·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD) | 1.371 | ||
| Viscosity | 1.22 mPa s | ||
| 1.74 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH | -483.88—483.16 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Std enthalpy of combustion ΔcH | -875.50—874.82 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Standard molar entropy S | 158.0 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
| Specific heat capacity, C | 123.1 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| G01AD02 (WHO) S02AA10 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 | | ||
| Explosive limits | 4–16% | ||
| U.S. Permissible exposure limit (PEL) | TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3)[7] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related {{{label}}} | {{{value}}} | ||
| Related compounds | {{{value}}} | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||

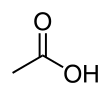
Acetic acid, or ethanoic acid, (CH3COOH) is a carboxylic acid. It is the main compound of vinegar, other than water.
It tastes and smells sour; it has no color. Its melting point is 16.5 °C(61.6 °F) and its boiling point is 118.1 °C(244.5 °F). It has a pH of 2.4.
Acetic acid is commonly used as a food additive. It has the E numbers E 260 (acetic acid).
Potassium acetate (E 261), sodium acetate (E 262), and calcium acetate (E 2639) are salts of acetic acid; they are commonly used to preserve food, usually vegetables. In sourdough, ethanol fermentation is used.
References
[change | change source]- ↑ Scientific literature reviews on generally recognised as safe (GRAS) food ingredients. National Technical Information Service. 1974. p. 1.
- ↑ "Chemistry", volume 5, Encyclopædia Britannica, 1961, page 374
- ↑ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 745. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ "acetic acid_msds".
- ↑ Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–88. ISBN 9781498754293.
- ↑ Bordwell, F. G.; Algrim, Donald (1976). "Nitrogen acids. 1. Carboxamides and sulfonamides". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 41 (14): 2507–2508. doi:10.1021/jo00876a042.
- ↑ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0002". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch