肥厚型心肌病變 - 维基百科,自由的百科全书
| 肥厚型心肌病變 | |
|---|---|
| 又称 | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; Asymmetric septal hypertrophy; idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis;[1] hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM) |
 | |
| 症状 | 疲勞、水肿和呼吸困难、胸痛或暈厥[2] |
| 併發症 | 心臟衰竭、心律不整和心臟驟停[3][4] |
| 病因 | 遗传学、法布瑞氏病、弗里德希氏共济失调和某些藥物[5][6] |
| 診斷方法 | 心电描记术, 超声心动描记术, 壓力測試和基因檢測[7] |
| 鑑別診斷 | 高血壓性心臟病、主動脈瓣狹窄、運動員心臟症候群[5] |
| 治療 | 藥物、植入式心律去顫器、手術[7] |
| 藥物 | β受体阻滞剂、维拉帕米和丙吡胺[8] |
| 预后 | 每年的死亡率小於 1%(接受治療的話)[9] |
| 患病率 | 平均每500年一位[8] |
| 分类和外部资源 | |
| 醫學專科 | 心血管內科 |
| ICD-11 | BC43.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 425.11、425.1 |
| OMIM | 192600 |
| DiseasesDB | 6373 |
| MedlinePlus | 000192 |
| eMedicine | 152913、890068、348503 |
| Orphanet | 217568、99739 |
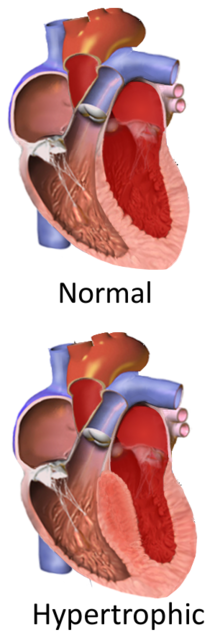
肥厚型心肌病變(Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,HCM)是一种心臟部分肥大而无明显原因的心臟病[8]。症状多样,从无症状到疲勞、水肿和呼吸困难[10]。也可能造成胸痛或暈厥[10]。并发症包括心臟衰竭、心律不整和心源性猝死[3] [4]。1958年,唐納德·蒂爾首次现代化地清楚描述此疾病[11] [12]。
病因
[编辑]最常见的病因是遺傳,由父母遗传給子女[6]。通常是制造心肌蛋白相关的某些基因發生突变[6]。其他可能原因包括法布瑞氏病、弗里德希氏共济失调,而某些药物(如:他克莫司)的副作用[5]。它是一种心肌病,受影响的主要部位是心肌[3]。心肌僵硬造成心脏輸出血液的能力下降,心室間隔增厚也会使血液从左心室流入主动脉時受阻,并导致二尖瓣功能减弱[13] [8]。
诊断方法
[编辑]依心电图和超声心动描记术诊断[14]。其他檢查可能包括壓力測試和基因檢測[14]。替患者的亲属進行基因筛查也可以提早診斷[14] [15]。治疗通常从β受体阻滞剂、维拉帕米和丙吡胺开始[8]。应谨慎使用利尿劑,因為它會减少左心室容量和流出量,反而使心臟的輸出變小,而使病情惡化[16]。对某些类型心律不整的患者,可能会建议使用植入式心律去顫器[14]。对其他處置無效的患者,可考慮手术,如:心室中隔心肌切除術或心脏移植[13] [17]。经过治疗,死于此病的风险每年不到 1%[9]。
发病人群
[编辑]每 200 人中就有 1 人患有肥厚型心肌病變[8] [17]。男性和女性的发病率大致相同[18]。所有年龄層都可能受發病[18]。
参考文獻
[编辑]- ^ Other Names for Cardiomyopathy. NHLBI. June 22, 2016 [31 August 2016]. (原始内容存档于28 July 2016).
- ^ What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Cardiomyopathy?. NHLBI. 22 June 2016 [10 November 2017]. (原始内容存档于28 July 2016).
- ^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 What Is Cardiomyopathy?. NHLBI. 22 June 2016 [10 November 2017]. (原始内容存档于10 November 2017).
- ^ 4.0 4.1 Barsheshet A, Brenyo A, Moss AJ, Goldenberg I. Genetics of sudden cardiac death. Current Cardiology Reports. October 2011, 13 (5): 364–76. PMID 21789574. S2CID 25887172. doi:10.1007/s11886-011-0209-y.
- ^ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Ferri, Fred F. Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2018 E-Book: 5 Books in 1. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2017: 246 [2017-11-10]. ISBN 9780323529570. (原始内容存档于2017-11-10).
- ^ 6.0 6.1 6.2 What Causes Cardiomyopathy?. NHLBI. 22 June 2016 [10 November 2017]. (原始内容存档于5 October 2017).
- ^ 7.0 7.1 Gersh BJ, Maron BJ, Bonow RO, Dearani JA, Fifer MA, Link MS, Naidu SS, Nishimura RA, Ommen SR, Rakowski H, Seidman CE, Towbin JA, Udelson JE, Yancy CW. 2011 ACCF/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. December 2011, 142 (6): 1303–1338. PMID 22093712. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2011.10.019
 .
. - ^ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 Cui, Hao; Schaff, Hartzell V. https://web.archive.org/web/20221013073118/https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=kcPPDwAAQBAJ&newbks=0&printsec=frontcover&pg=PA735
|archiveurl=缺少标题 (帮助). Raja, Shahzad G. (编). 80. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Switzerland: Springer. 2020: 735–748 [2022-10-13]. ISBN 978-3-030-24176-6. (原始内容存档于2022-10-13) (英语). - ^ 9.0 9.1 Maron BJ, Ommen SR, Semsarian C, Spirito P, Olivotto I, Maron MS. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: present and future, with translation into contemporary cardiovascular medicine. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. July 2014, 64 (1): 83–99. PMID 24998133. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2014.05.003
 .
. - ^ 10.0 10.1 What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Cardiomyopathy?. NHLBI. National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. 24 March 2022 [13 October 2022]. (原始内容存档于28 July 2016).
- ^ Teare D. Asymmetrical hypertrophy of the heart in young adults. British Heart Journal. January 1958, 20 (1): 1–8. PMC 492780
 . PMID 13499764. doi:10.1136/hrt.20.1.1.
. PMID 13499764. doi:10.1136/hrt.20.1.1. - ^ McKenna WJ, Sen-Chowdhry S. From Teare to the present day: a fifty year odyssey in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a paradigm for the logic of the discovery process. Revista Espanola de Cardiologia. December 2008, 61 (12): 1239–44 [2017-02-06]. PMID 19080961. doi:10.1016/S1885-5857(09)60050-5. (原始内容存档于2017-11-11).
- ^ 13.0 13.1 AHA. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM). www.heart.org. American Heart Association. 13 May 2022 [13 October 2022]. (原始内容存档于6 October 2022) (英语).
- ^ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 Ommen, Steve R.; Mital, Seema; Burke, Michael A.; Day, Sharlene M.; Deswal, Anita; Elliott, Perry; Evanovich, Lauren L.; Hung, Judy; Joglar, José A.; Kantor, Paul; Kimmelstiel, Carey. 2020 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Executive Summary. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 22 December 2020, 76 (25): 3022–3055 [14 October 2022]. PMID 33229115. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2020.08.044. (原始内容存档于16 October 2022).
- ^ Phelan, Dermot M.; Symanski, John. EngelEngel, David J.; Phelan, Dermot M. , 编. 7. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Switzerland: Springer. 2021: 97–110 [2022-10-14]. ISBN 978-3-030-69383-1. (原始内容存档于2022-10-14) (英语).
- ^ Shah, Sandy N. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Treatment & Management: Approach Considerations, Left Ventricular Myomectomy and Mitral Valve Replacement, Pacemaker Implantation. emedicine. 29 April 2022 [13 October 2022]. (原始内容存档于13 October 2022).
- ^ 17.0 17.1 Ralph-Edwards, Anthony; Vanderlaan, Rachel D.; Bajona, Pietro. Transaortic septal myectomy: techniques and pitfalls. Annals of Cardiothoracic Surgery. July 2017, 6 (4): 410–415 [2022-10-13]. ISSN 2225-319X. PMID 28944183. doi:10.21037/acs.2017.07.08. (原始内容存档于2022-10-13).
- ^ 18.0 18.1 Types of Cardiomyopathy. NHLBI. 22 June 2016 [10 November 2017]. (原始内容存档于4 October 2017).
外部連結
[编辑]- GeneReviews/NIH/NCBI/UW entry on Familial Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Overview
- National Heart, Blood, and Lung Institute Cardiomyopathy Page


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch