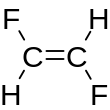
1,2-Difluoroethylene
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1,2-Difluoroethene | |||
| Other names 1,2-Difluoroethylene sym-Difluoroethylene Ethene, 1,2-difluoro-,(Z)- cis-Difluoroethene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H2F2 | |||
| Molar mass | 64.035 g·mol−1 | ||
| Boiling point | -36.0±8.0 °C | ||
| -60.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
1,2-Difluoroethylene, also known as 1,2-difluoroethene, is an organofluoride with the molecular formula C2H2F2. It can exist as either of two geometric isomers, cis-1,2-difluoroethylene or trans-1,2-difluoroethylene.
It is regarded as a hazardous chemical for being toxic by inhalation, and a volatile chemical, and it causes irritation when it comes into contact with the skin and mucous membranes.
E-Z relative stability
[edit]For most 1,2-disubstituted compounds that exhibit cis–trans isomerism, the trans (E) isomer is more stable than the cis (Z) isomer. However, 1,2-difluoroethylene has the opposite situation, with the cis more stable than the trans by 0.9 kcal/mol.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Craig, Norman C.; Entemann, Eric A. (July 1961). "Thermodynamics of cis-trans Isomerizations. The 1,2-Difluoroethylenes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 83 (14): 3047–3050. doi:10.1021/ja01475a019.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch