Gordus (Lydia)
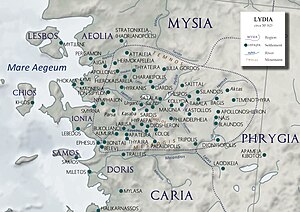
Gordus or Gordos (Ancient Greek: Γόρδος),[1] also known as Julia Gordus or Iulia Gordos, and possibly also known as Porotta,[2][3] was an ancient Greek city located in eastern Lydia (modern western Turkey). It was a strategically important town founded by the Seleucid Kings. The Julio-Claudian emperors of the Roman Empire renamed the city Julia Gordos in the 1st century and the city minted its own coins.[4][5][6]
The city achieved the full status of a polis under the Flavian emperors.[7]
It was the home to Appolophanes the physician,[8] and there is epigraphical evidence of both pagans[9] and Christians in the town.[10]
Three bishops of the town are known: Isidor attended Third Council of Constantinople, Neophytus attended the Second Council of Nicaea and Stephen attended the Photian Council of 870. No longer the seat of a residential bishop, it remains a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church.[11]
Its site is located near Eski Gördes in Asiatic Turkey.[2][3]
References
[edit]- ^ Hierocles. Synecdemus. Vol. p. 671.
- ^ a b Richard Talbert, ed. (2000). Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World. Princeton University Press. p. 56, and directory notes accompanying. ISBN 978-0-691-03169-9.
- ^ a b Lund University. Digital Atlas of the Roman Empire.
- ^ Getzel M. Cohen, The Hellenistic Settlements in Europe, the Islands, and Asia Minor (University of California Press, 2 Nov. 1996)p209.
- ^ Gordos-Julia in Lydia, Trajan, Coins.
- ^ Coin of Julia Gordos under Antoninus Pius.
- ^ Getzel M. Cohen, The Hellenistic Settlements in Europe, the Islands, and Asia Minor (University of California Press, 2 Nov. 1996)p210.
- ^ Vivian Nutton, Ancient Medicine (Routledge, 2012) p409.
- ^ H. Malay, Great Antiochose Basic Apollophanes A Adjusted To Zeus Around Gordos.
- ^ Peter Thonemann, Inscriptions from Hadrianopolis, Tieion, Iulia Gordos and Toriaion, P H I L I A - International Journal of Ancient Mediterranean Studies Volume 1 • 2015 p82-83[permanent dead link].
- ^ Catholic Hierarchy


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch