Kherson Oblast
Kherson Oblast Херсонська область | |
|---|---|
| Khersonska oblast[1] | |
| | |
| Nickname: Херсонщина (Khersonshchyna) | |
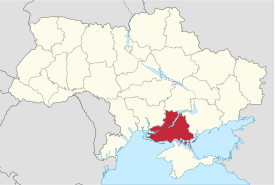 Pre-July 2020 boundary shown | |
| Country | Ukraine |
| Established | 1944 |
| Administrative center | Kherson |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Oleksandr Prokudin[2][b] |
| • Oblast council | 64 seats |
| • Chairperson | Oleksandr Samoylenko |
| Area | |
• Total | 28,461 km2 (10,989 sq mi) |
| Population (2022)[3] | |
• Total | 1,001,598 |
| • Rank | Ranked 22nd |
| • Density | 35/km2 (91/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | ₴ 88 billion (€2.3 billion) |
| • Per capita | ₴ 87,378 (€2,300) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Area code | +380-55 |
| ISO 3166 code | UA-65 |
| Vehicle registration | ВT |
| Raions | 5 |
| Cities (total) | 9 |
| • Regional cities | 3 |
| Urban-type settlements | 30 |
| Villages | 658 |
| HDI (2022) | 0.740[5] high |
| FIPS 10-4 | UP08 |
| NUTS statistical regions of Ukraine | UA43 |
| Website | khoda.gov.ua |
Kherson Oblast (Ukrainian: Херсонська область, romanized: Khersonska oblast, IPA: [xerˈsɔnʲsʲkɐ ˈɔblɐsʲtʲ]; Russian: Херсонская область), also known as Khersonshchyna (Херсонщина, IPA: [xerˈsɔnʃtʃɪnɐ]), is an oblast (province) in southern Ukraine. It is located just north of Crimea. Its administrative center is Kherson, on the northern or right bank of the Dnieper river, which bisects the oblast. The oblast has an area of 28,461 km2 and a population of 1,001,598 (2022 estimate).[3] It is considered the 'fruit basket' of the country, as much of its agricultural production is dispersed throughout the country, with production peaking during the summer months.
Most of the area of the oblast has been under Russian military occupation since early in the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. In September 2022, Russia claimed to have annexed Kherson Oblast after arranging a disputed referendum. The referendum and the subsequent claimed annexation are internationally unrecognized. As the result of a counteroffensive operation, Ukrainian forces retook the whole area on the right bank of the Dnieper, including Kherson city, by mid-November 2022.
History

At various times throughout its history, the territory was ruled either entirely or partly by Scythia, ancient Greeks, Old Great Bulgaria, Khazars, Kipchaks, the Byzantine Empire, Kyivan Rus', Italians,[6] the Mongol Empire, Lithuania, the Crimean Khanate, the Ottoman Empire, Poland[7] and Russia. In medieval times, the towns of greatest importance were Oleshia, a former Byzantine, Kyivan Rus' and Genoese trading port,[6] and Tawan/Kazikermen, a former Lithuanian customs point and Polish and Turkish fortress, which is now Beryslav.[7] Another notable town in the early modern period was Bilchowisce, now Kherson.[8]
In 1917–1920 the territory was variously controlled by the Ukrainians, Bolsheviks and White Russians, decisively becoming part Soviet Ukraine in 1920. It was the scene of Soviet genocidal crimes, chiefly the Holodomor of 1932–1933, and part of the Katyn massacre of 1940.[9] During World War II, it was occupied by Germany from 1941 to 1944.
The province was established in 1944 within Soviet Ukraine. In the 1991 Ukrainian independence referendum, 90.13% of votes in Kherson Oblast were in favor of the Declaration of Independence of Ukraine.[10]
A survey conducted by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology in December 2014 found that 90.9% of the oblast's population opposed their region joining Russia, 1% supported the idea, and the rest were undecided or did not respond.[10][11]
Russian invasion
As a result of the 24 February 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, Russian forces occupied most of the oblast. Russian-controlled parts of the oblast were governed by the "Kherson military–civilian administration"[12] from 28 April to 30 September 2022.
On 27 July 2022, the Ukrainian army destroyed the Antonivka Road Bridge, as part of its wider campaign to isolate the Russian forces on the right bank of the Dnieper river.[13]
On 23–27 September 2022, the Russian Federation held referendums in the occupied territories of Kherson oblast for the "independence and subsequent entry into the Russian Federation". Most states recognized the referendums to be staged and against international law.[citation needed]
On 29 September, the Russian Federation recognized Kherson Oblast as an independent state.[14] The next day, Russian president Vladimir Putin announced the annexation of the Kherson Oblast and signed an "accession decree" that is widely considered to be illegal.[15] At that time, Russia was not in control of the province as a whole.[16]
The United Nations General Assembly subsequently passed a resolution calling on countries not to recognise what it described as an "attempted illegal annexation" and demanded that Russia "immediately, completely and unconditionally withdraw".[17]
By 11 November 2022, the city of Kherson and all the Russian-held territory on the right bank of the Dnieper had been recaptured by Ukrainian forces.[18] The territory on the left bank is still under Russian control.
On 6 June 2023, the Kakhovka Dam was breached, causing extensive flooding downstream and prompting mass evacuations in the oblast, while the Kakhovka Reservoir was drained.[19]
Russian authorities claimed that Russian President Vladimir Putin won 88.12% of the vote in the occupied Kherson region in the 2024 Russian presidential election,[20] which has been described as rigged and fraudulent.[21]
Geography

Kherson Oblast is bordered by Dnipropetrovsk Oblast to the north, the Black Sea and Crimea to the south, Mykolaiv Oblast to the west, and the Azov Sea and Zaporizhzhia Oblast to the east. The Dnieper River, which includes the Kakhovka Reservoir, runs through the oblast.
Before the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, two bridges spanned the Dniper: the Kakhovka Bridge near Nova Kakhovka and the Antonivka Road Bridge at Kherson. Another significant bridge, the Daryivka Bridge crosses the Inhulets river and connects Kherson via the M14 highway to Beryslav, the other abutment of the Kakhovka Bridge.
The oblast's Henichesk Raion includes the northern portion of the Arabat Spit, a thin strip of land between the brackish Syvash and the Sea of Azov that is geographically part of the Crimean Peninsula. Due to Russia gaining de facto control of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea in 2014, this strip within Kherson Oblast was the only part of the Crimean Peninsula under Ukrainian control immediately prior to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.[citation needed]
Historically, it is located in Yedisan (north-western part), Zaporizhzhia (northern part) and Pryazovia (southern and eastern parts).
Kherson is the only city in the oblast with a population over 100,000. Four other cities have over 30,000; they are, in order from largest, Nova Kakhovka, Kakhovka, Oleshky and Henichesk.
Administrative divisions
Until the 2020 re-organisation, the Kherson Oblast was administratively subdivided into 18 raions (districts) and 3 municipalities. The municipalities – Kherson (administrative center of the oblast), Nova Kakhovka, and Kakhovka – were directly subordinate to the oblast government. The Kherson municipality was subdivided into 3 urban districts. All information below was current as of 2015.[22]
| Name | Ukrainian name | Area (km2) | Population 2015 | Admin. center | Urban population only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kherson | Херсон (місто) | 423 | 333,737 | Kherson | 322,260 |
| Hola Prystan | Гола Пристань (місто) | 9 | 14,883 | Hola Prystan | 14,568 |
| Nova Kakhovka | Нова Каховкa (місто) | 223 | 68,205 | Nova Kakhovka | 62,128 |
| Kakhovka | Каховкa (місто) | 16 | 36,958 | Kakhovka | 36,958 |
| Beryslav Raion | Бериславський (район) | 1,721 | 48,025 | Beryslav | 16,682 |
| Bilozerka Raion | Білозерський (район) | 1,534 | 66,564 | Bilozerka | 9,739 |
| Chaplynka Raion | Чаплинський (район) | 1,722 | 35,219 | Chaplynka | 12,638 |
| Henichesk Raion | Генічеський (район) | 3,008 | 59,991 | Henichesk | 33,748 |
| Hola Prystan Raion | Голопристанський (район) | 3,411 | 45,827 | Hola Prystan | 14,666 |
| Hornostaivka Raion | Горностаївський (район) | 1,018 | 19,788 | Hornostaivka | 6,681 |
| Ivanivka Raion | Іванівський (район) | 1,120 | 13,995 | Ivanivka | 4,560 |
| Kalanchak Raion | Каланчацький (район) | 916 | 21,568 | Kalanchak | 11,169 |
| Kakhovka Raion | Каховський (район) | 1,450 | 35,968 | Kakhovka | N/A * |
| Novotroitske Raion | Новотроїцький (район) | 2,298 | 35,921 | Novotroitske | 14,979 |
| Novovorontsovka Raion | Нововоронцовський (район) | 1,005 | 21,442 | Novovorontsovka | 6,379 |
| Nyzhni Sirohozy Raion | Нижньосірогозький (район) | 1,209 | 15,985 | Nyzhni Sirohozy | 4,891 |
| Oleshky Raion | Олешківський (район) | 1,759 | 71,888 | Oleshky | 36,317 |
| Skadovsk Raion | Скадовський (район) | 1,456 | 47,930 | Skadovsk | 21,830 |
| Velyka Lepetykha Raion | Великолепетиський (район) | 1,000 | 16,827 | Velyka Lepetykha | 8,326 |
| Velyka Oleksandrivka Raion | Великоолександрівський (район) | 1,540 | 25,948 | Velyka Oleksandrivka | 9,747 |
| Verkhniy Rohachyk Raion | Верхньорогачицький (район) | 915 | 12,003 | Verkhniy Rohachyk | 5,698 |
| Vysokopillia Raion | Високопільський (район) | 701 | 15,121 | Vysokopillia | 6,148 |

.* Note: Though the administrative center of the raion is housed in the city/town that it is named after, cities do not answer to the raion authorities only towns do; instead they are directly subordinated to the oblast government and therefore are not counted as part of raion statistics.
At a lower level of administration, these district-level administrations are subdivided into:
- Settlements – 697, including:
- Villages – 658; – See List of villages in Kherson Oblast
- Cities/Urban-type settlements – 36, including:
- Selsovets – 260.
The local administration of the oblast is controlled by the Kherson Regional Council. The governor of the oblast is the Kherson Regional Council speaker, appointed by the President of Ukraine.
Demographics



| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 1,029,988 | — |
| 1979 | 1,163,435 | +13.0% |
| 1989 | 1,239,969 | +6.6% |
| 2001 | 1,175,122 | −5.2% |
| 2011 | 1,088,237 | −7.4% |
| 2022 | 1,001,598 | −8.0% |
| Source: [23][24] | ||
The population of the oblast is 1,083,367 (2012), which is 2.4% of the total population of Ukraine. It is also ranked 21st by its population. The population density is 38 per km2.
About 61.5% or 745,400 people live in urban areas of the Oblast and 38.5% or 467,600 people live in agricultural centers/villages. Men make up 46.7% or 565,400 people of the population, women make up 53.3% or 644,600 people, and pensioners make up 26.2% or 317,400 people of the oblast population.
Ukrainian National Census (2001):
- Ukrainians – 82.0%
- Russians – 14.1%
- Belarusians – 0.7%
- Meskhetian Turks – 0.5%
- Crimean Tatars – 0.5%
- Others – 2.2%
Age structure
- 0–14 years: 15.1%
 (male 83,397/female 79,303)
(male 83,397/female 79,303) - 15–64 years: 70.5%
 (male 364,907/female 393,933)
(male 364,907/female 393,933) - 65 years and over: 14.4%
 (male 50,404/female 104,856) (2013 official)
(male 50,404/female 104,856) (2013 official)
Median age
- total: 39.5 years

- male: 36.2 years

- female: 42.7 years
 (2013 official)
(2013 official)
Attractions
Gallery
- The building of the former Kherson City Duma
- Palace of Culture, Nova Kakhovka
- Church of the Presentation of Mary, Beryslav
- Ohuz Kurgan
- Kakhovka Arboretum
- The Dnieper River in Kherson
- Oleshky Sands near Radensk
- The Dzharylhach Lighthouse
- Lake Syvash at night
See also
Notes
- ^ Partially annexed by Russia as Kherson Oblast
- ^ Control over Kherson Oblast is disputed due to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. In the Russian-occupied part of the Oblast, the governor is Vladimir Saldo. Prokudin is the governor recognized by Ukraine.
References
- ^ Syvak, Nina; Ponomarenko, Valerii; Khodzinska, Olha; Lakeichuk, Iryna (2011). Veklych, Lesia (ed.). Toponymic Guidelines for Map and Other Editors for International Use (PDF). scientific consultant Iryna Rudenko; reviewed by Nataliia Kizilowa; translated by Olha Khodzinska. Kyiv: DerzhHeoKadastr and Kartographia. p. 20. ISBN 978-966-475-839-7. Retrieved 6 October 2020 – via United Nations Statistics Division.
- ^ Zelenskyy appoints three chairmen of Oblast Military Administrations, Ukrainska Pravda (7 February 2023)
- ^ a b Чисельність наявного населення України на 1 січня 2022 [Number of Present Population of Ukraine, as of January 1, 2022] (PDF) (in Ukrainian and English). Kyiv: State Statistics Service of Ukraine. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 July 2022.
- ^ "Валовии регіональнии продукт".
- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org.
- ^ a b "Oleshia". encyclopediaofukraine.com. Retrieved 23 May 2024.
- ^ a b Słownik geograficzny Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów słowiańskich, Tom XII (in Polish). Warszawa. 1892. p. 266.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Moll, Herman (1701). A System Of Geography: Or, A New & Accurate Description Of The Earth In all its Empires, Kingdoms and States. Illustrated with History and Topography, And Maps of every Country, Fairly Engraven on Copper, according to the latest Discoveries and Corrections. London. p. 442.
- ^ Zbrodnia katyńska (in Polish). Warszawa: IPN. 2020. p. 17. ISBN 978-83-8098-825-5.
- ^ a b Лише 3% українців хочуть приєднання їх області до Росії [Only 3% of Ukrainians want their region to become part of Russia]. Dzerkalo Tyzhnia (in Ukrainian). 3 January 2015.
- ^ "Press releases and reports – the views and opinions of South-Eastern regions residents of Ukraine: April 2014".
- ^ "Russia-Appointed Official In Ukraine Killed In Car Bombing". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 24 August 2022.
- ^ Axe, David (29 July 2022). "In Southern Ukraine, Kyiv's Artillery Drops Bridges And Isolates A Whole Russian Army". Forbes.
- ^ "Официальное опубликование правовых актов ∙ Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации". Archived from the original on 6 October 2022. Retrieved 30 September 2022.
- ^ "Putin annexes four regions of Ukraine in major escalation of Russia's war". the Guardian. 30 September 2022. Retrieved 30 September 2022.
- ^ "Factbox: The four regions that Russia is poised to annex from Ukraine". Reuters. 30 September 2022. Retrieved 30 September 2022.
- ^ "Ukraine: UN General Assembly demands Russia reverse course on 'attempted illegal annexation'". 12 October 2022.
- ^ Santora, Marc (14 November 2022). "Zelensky Visits Kherson After Russian Retreat Turns River Into New Front Line". The New York Times. Retrieved 14 November 2022.
- ^ "Ukraine dam: What we know about Nova Kakhovka incident". BBC News. 8 June 2023. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ Vasilyeva, Olga (20 March 2024). "The election that wasn't". Novaya Gazeta Europe.
- ^ "The extent of fraud in Russia's presidential election begins to emerge". Le Monde. 20 March 2024.
- ^ "Population Quantity". UkrStat (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- ^ "Division of Ukraine".
- ^ "Ukraine: Provinces and Major Cities".
External links
- Portal of Kherson
- Site of Kherson nationalists
- State Administration of Kherson Region – official site (in Ukrainian)
- Information Card of the Region – official site of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine
- Promo-video about Kherson and South of Ukraine – official YouTube channel of The center of tourism and adventures "ХерсON"


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch











