LGBTQ rights by country or territory

| Same-sex intercourse illegal. Penalties: | |
Prison; death not enforced | |
Death under militias | Prison, with arrests or detention |
Prison, not enforced1 | |
| Same-sex intercourse legal. Recognition of unions: | |
Extraterritorial marriage2 | |
Limited foreign | Optional certification |
None | Restrictions of expression, not enforced |
Restrictions of association with arrests or detention | |
1No imprisonment in the past three years or moratorium on law.
2Marriage not available locally. Some jurisdictions may perform other types of partnerships.

| | Neither | States which did not support either declaration |
| | Non-member states | States that are not voting members of the United Nations |
| | Oppose | States which supported an opposing declaration in 2008 and continued their opposition in 2011 |
| | Subsequent member | South Sudan, did not exist in 2008 |
| | Support | States which supported the LGBT rights declaration in the General Assembly or on the Human Rights Council in 2008 or 2011 |
| Part of a series on |
| LGBTQ rights |
|---|
 |
| Lesbian ∙ Gay ∙ Bisexual ∙ Transgender ∙ Queer |
| |
| Rights |
|---|
 |
| Theoretical distinctions |
| Human rights |
| Rights by beneficiary |
| Other groups of rights |
|
| Part of a series on |
| LGBTQ topics |
|---|
| |
| Part of a series on |
| Discrimination |
|---|
 |
Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.

Notably, as of May 2024[update], 37 countries recognize same-sex marriage.[1][2] By contrast, not counting non-state actors and extrajudicial killings, only two countries are believed to impose the death penalty on consensual same-sex sexual acts: Iran and Afghanistan.[3][4][5][6] The death penalty is officially law, but generally not practiced, in Mauritania, Saudi Arabia, Somalia (in the autonomous state of Jubaland) and the United Arab Emirates.[7][8] LGBT people also face extrajudicial killings in the Russian region of Chechnya.[9] Sudan rescinded its unenforced death penalty for anal sex (hetero- or homosexual) in 2020. Fifteen countries have stoning on the books as a penalty for adultery, which (in light of the illegality of gay marriage in those countries) would by default include gay sex, but this is enforced by the legal authorities in Iran and Nigeria (in the northern third of the country).[10][11][12][13][14]
In 2011, the United Nations Human Rights Council passed its first resolution recognizing LGBT rights, following which the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights issued a report documenting violations of the rights of LGBT people, including hate crimes, criminalization of homosexual activity, and discrimination. Following the issuance of the report, the United Nations urged all countries which had not yet done so to enact laws protecting basic LGBT rights.[15][16] A 2022 study found that LGBT rights (as measured by ILGA-Europe's Rainbow Index) were correlated with less HIV/AIDS incidence among gay and bisexual men independently of risky sexual behavior.[17]
The 2023 Equaldex Equality Index ranks the Nordic countries, Chile, Uruguay, Canada, the Benelux countries, Spain, Andorra, and Malta among the best for LGBT rights. The index ranks Nigeria, Yemen, Brunei, Afghanistan, Somalia, Mauritania, Palestine, and Iran among the worst.[18][better source needed] Asher & Lyric ranked Canada, Sweden, and the Netherlands as the three safest nations for LGBT people in its 2023 index.[19]
Scope of laws
Laws that affect LGBT people include, but are not limited to, the following:
- laws concerning the recognition of same-sex relationships, including same-sex marriage, civil unions, and domestic partnerships
- laws concerning same-sex parenting, including same-sex adoption
- anti-discrimination laws in employment, housing, education, public accommodations
- anti-bullying legislation to protect LGBT children at school
- hate crime laws imposing enhanced criminal penalties for prejudice-motivated violence against LGBT people
- bathroom bills affecting access to sex-segregated facilities by transgender people
- laws related to sexual orientation and military service
- laws concerning access to assisted reproductive technology
- sodomy laws that penalize consensual same-sex sexual activity. These may or may not target homosexuals, males or males and females, or leave some homosexual acts legal.
- adultery laws that same-sex couples are subject to
- age of consent laws that may impose higher ages for same-sex sexual activity
- laws regarding donation of blood, corneas, and other tissues by men who have sex with men
- laws concerning access to gender-affirming surgery and gender-affirming hormone replacement therapy
- legal recognition and accommodation of the affirmed gender.
History of LGBT-related laws
Ancient India
Ayoni or non-vaginal sex of all types is punishable in the Arthashastra. Homosexual acts are, however, treated as a smaller offence punishable by a fine, while unlawful heterosexual sex carries much harsher punishment. The Dharmsastras, especially the later ones, prescribe against non-vaginal sex like the Vashistha Dharmasutra. The Yājñavalkya Smṛti prescribes fines for such acts including those with other men. Manusmriti prescribes light punishments for such acts.[20][21] Vanita states that the verses about punishment for a sex between female and a maiden is due to its strong emphasis on a maiden's sexual purity.[22]
Ancient Israel
The ancient Law of Moses (the Torah) forbids people from lying with people of the same sex (i.e., from having intercourse) in Leviticus 18 and gives a story of attempted homosexual rape in Genesis 19, in the story of Sodom and Gomorrah, after which the cities were soon destroyed with "brimstone and fire, from the Lord"[23][24] and the death penalty was prescribed to its inhabitants – and to Lot's wife, who was turned into a pillar of salt because she turned back to watch the cities' destruction.[25][26] In Deuteronomy 22:5, cross-dressing is condemned as "abominable".[27][28]
Assyria
In Assyrian society, sex crimes were punished identically whether they were homosexual or heterosexual.[29] An individual faced no punishment for penetrating someone of equal social class, a cult prostitute, or with someone whose gender roles were not considered solidly masculine.[29] Such sexual relations were even seen as good fortune, with an Akkadian tablet, the Šumma ālu, reading, "If a man copulates with his equal from the rear, he becomes the leader among his peers and brothers".[30][31] However, homosexual relationships with fellow soldiers, slaves, royal attendants, or those where a social better was submissive or penetrated, were treated as bad omens.[32][33]
Middle Assyrian Law Codes dating 1075 BC has a particularly harsh law for homosexuality in the military, which reads: "If a man have intercourse with his brother-in-arms, they shall turn him into a eunuch."[34][35] A similar law code reads, "If a seignior lay with his neighbor, when they have prosecuted him (and) convicted him, they shall lie with him (and) turn him into a eunuch". This law code condemns a situation that involves homosexual rape. Any Assyrian male could visit a prostitute or lie with another male, just as long as false rumors or forced sex were not involved with another male.[36]
Ancient Rome
In ancient Rome, the bodies of citizen youths were strictly off-limits, and the Lex Scantinia imposed penalties on those who committed a sex crime (stuprum) against a freeborn male minor.[37] Acceptable same-sex partners were males excluded from legal protections as citizens: slaves, male prostitutes, and the infames, entertainers or others who might be technically free but whose lifestyles set them outside the law.
A male citizen who willingly performed oral sex or received anal sex was disparaged, but there is only limited evidence of legal penalties against these men.[38] In courtroom and political rhetoric, charges of effeminacy and passive sexual behaviors were directed particularly at "democratic" politicians (populares) such as Julius Caesar and Mark Antony.[39]
Roman law addressed the rape of a male citizen as early as the 2nd century BC when it was ruled that even a man who was "disreputable and questionable" had the same right as other citizens not to have his body subjected to forced sex.[40] A law probably dating to the dictatorship of Julius Caesar defined rape as forced sex against "boy, woman, or anyone"; the rapist was subject to execution, a rare penalty in Roman law.[41] A male classified as infamis, such as a prostitute or actor, could not as a matter of law be raped, nor could a slave, who was legally classified as property; the slave's owner, however, could prosecute the rapist for property damage.[42]
In the Roman army of the Republic, sex among fellow soldiers violated the decorum against intercourse with citizens and was subject to harsh penalties, including death,[43] as a violation of military discipline.[44] The Greek historian Polybius (2nd century BC) lists deserters, thieves, perjurers, and "...on young men who have abused their persons" as subject to the fustuarium, clubbing to death.[45] Ancient sources are most concerned with the effects of sexual harassment by officers, but the young soldier who brought an accusation against his superior needed to show that he had not willingly taken the passive role or prostituted himself.[46] Soldiers were free to have relations with their male slaves;[47] the use of a fellow citizen-soldier's body was prohibited, not homosexual behaviors per se.[48] By the late Republic and throughout the Imperial period, there is increasing evidence that men whose lifestyle marked them as "homosexual" in the modern sense served openly.[49]
Although Roman law did not recognize marriage between men, and in general Romans regarded marriage as a heterosexual union with the primary purpose of producing children, in the early Imperial period some male couples were celebrating traditional marriage rites. Juvenal remarks with disapproval that his friends often attended such ceremonies.[50] The emperor Nero had two marriages to men, once as the bride (with a freedman Pythagoras) and once as the groom. His consort Sporus appeared in public as Nero's wife wearing the regalia that was customary for the Roman empress.[51]
Apart from measures to protect the prerogatives of citizens, the prosecution of homosexuality as a general crime began in the 3rd century of the Christian era when male prostitution was banned by Philip the Arab. By the end of the 4th century, after the Roman Empire had come under Christian rule, passive homosexuality was punishable by burning.[52] "Death by sword" was the punishment for a "man coupling like a woman" under the Theodosian Code.[53] Under Justinian, all same-sex acts, passive or active, no matter who the partners are, were declared contrary to nature and punishable by death.[54]
British Empire
The United Kingdom introduced anti-homosexuality laws throughout its colonies, particularly in the 19th century when the British Empire was at its peak.[55] As of 2018, more than half of the 71 countries that criminalised homosexuality were former British colonies or protectorates.[56]
Netherlands
In 2001, the Netherlands was the first country in the world to legalize same-sex marriage.[57]
Global LGBT rights maps
Note that for simplicity the table below does not distinguish between 'legal' and 'lawful'. An action can only be legal or illegal where a specific law has been passed.
| Laws regarding same-sex sexuality by country or territory | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Worldwide laws regarding same-sex intercourse, unions and expression
1No imprisonment in the past three years or moratorium on law. 2Marriage not available locally. Some jurisdictions may perform other types of partnerships. | ||||||||||||||||||||
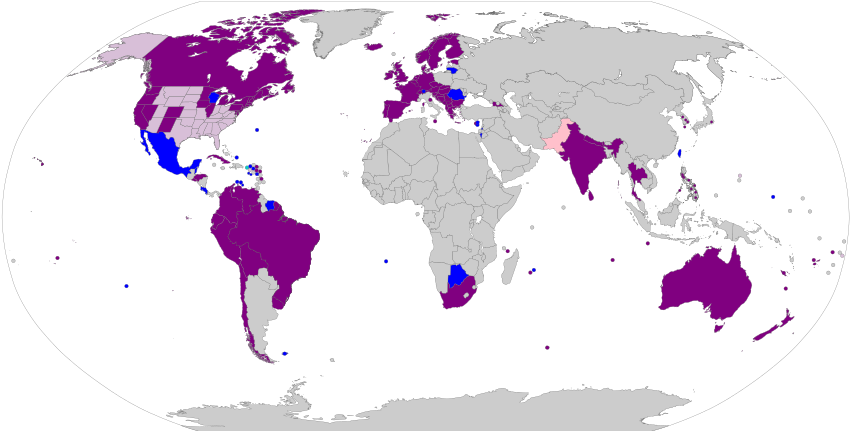
| LGBT rights at the United Nations |
|---|
 Support Countries which have signed a General Assembly declaration of LGBT rights or sponsored the Human Rights Council's 2011 resolution on LGBT rights (96 members) Oppose Countries which signed a 2008 statement opposing LGBT rights (initially 57 members, now 54 members after withdrawal of Fiji, Rwanda and Sierra Leone) Neither Countries which, as regards the UN, have expressed neither official support nor opposition to LGBT rights (44 members) |
| Homosexual "propaganda" and "morality" laws by country or territory |
|---|
 Countries or territories that do not have homosexual "propaganda" or "morality" laws Fine[58] Imprisonment |
| Decriminalization of same-sex sexual intercourse by country or territory |
|---|
| Equalization of age of consent laws for same-sex couples by country or territory |
|---|
 1790–1829 1830–1839 1840–1859 1860–1869 1870–1879 1880–1889 1890–1929 1930–1939 1940–19491 1950–1959 1960–1969 1970–1979 1980–1989 1990–1999 2000–2009 2010–2019 2020–present Unknown date for equal age of consent laws for opposite and same-sex couples No consent laws/equal age of consent laws always equal for opposite and same-sex couples Unequal age of consent laws for same-sex couples Same-sex sexual intercourse illegal 1During World War II, Nazi Germany annexed or occupied territory, extending Germany's laws against same-sex sexual intercourse. Age of consent was previously equalized for same-sex couples in the following countries or territories before the war: Belluno (legal in 1890), Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol (legal in 1890), Friuli-Venezia Giulia (legal in 1890),[59][60] and Poland (decriminalized in 1932).[61][62] During World War II Germany did not consistently enforce anti-homosexual laws in all occupied countries.[63][64] All countries and territories listed that were annexed or established into reichskommissariats by Nazi Germany during World War II were restored as independent countries or reincorporated into their previous countries during or after the war and thus re-legalized equal age of consent laws for same-sex couples in those areas.[citation needed] |
| Legal status of same-sex marriage |
|---|
 Marriage open to same-sex couples Mixed jurisdiction: marriage recognized by the state but not by tribal government for residents who are members of the tribe Legislation or binding domestic court ruling establishing same-sex marriage, but marriage is not yet provided for Same-sex marriage recognized with full rights when performed in certain other jurisdictions Civil unions or domestic partnerships Limited legal recognition Local certification without legal force Limited recognition of marriage performed in certain other jurisdictions (residency rights for spouses) Country subject to an international court ruling that recognizes same-sex marriage Other countries where same-sex unions are not legally recognized |
| Legal status of adoption by same-sex couples by country or territory |
|---|
| LGBT service in national militaries by country or territory |
|---|
| Employment discrimination laws by sexual orientation or gender identity by country or territory |
|---|
 Sexual orientation and gender identity: all employment Sexual orientation with anti–employment discrimination ordinance and gender identity solely in public employment Sexual orientation: all employment Gender identity: all employment Sexual orientation and gender identity: federal public employment and federal contractors Sexual orientation and gender identity: public employment Sexual orientation: public employment No national-level employment laws covering sexual orientation or gender identity |
| Anti-discrimination laws covering goods and services by sexual orientation and/or gender identity by country or territory |
|---|
 Sexual orientation and gender identity covered Sexual orientation covered Gender identity covered No national or local level anti-discrimination laws covering sexual orientation and/or gender identity in goods and services |
| Constitutional discrimination laws by sexual orientation and/or gender identity by country or territory |
|---|
| LGBT hate crime laws by country or territory |
|---|
| Incitement to hatred based on sexual orientation and gender identity prohibited by country or territory |
|---|
| Legal status on conversion therapy for minors on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity by country or territory |
|---|
 Ban on conversion therapy on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity De facto ban on conversion therapy No ban on conversion therapy |
| Immigration equality by country or territory[citation needed] |
|---|
| Bans on same-sex unions by country or territory |
|---|
 No specific prohibition of same-sex marriages or unions Same-sex marriage banned by secular constitution Same-sex marriage banned by constitutionally mandated religious law |
| Blood donation policies for men who have sex with men by country or territory |
|---|
 Men who have sex with men may donate blood; No deferral Men who have sex with men may donate blood; Temporary deferral Men who have sex with men may not donate blood; Permanent deferral No Data |
| Blood donation policies for female sex partners of men who have sex with men by country or territory |
|---|
 Female sex partners of men who have sex with men may donate blood; No deferral Female sex partners of men who have sex with men may donate blood; Temporary deferral Female sex partners of men who have sex with men may not donate blood; Permanent deferral No Data |
| Laws concerning gender identity-expression by country or territory |
|---|
| Legal recognition of non-binary genders and third gender |
|---|
Timeline
LGBT-related laws by country or territory
Africa
| List of countries or territories by LGBT rights in Africa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This table: Northern Africa
Western Africa
|


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch







