Eosuchus
| Eosuchus Temporal range: Late Paleocene - Early Eocene, | |
|---|---|
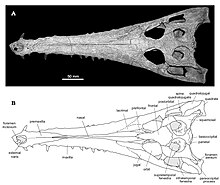 | |
| Holotype E. lerichei skull | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Archosauria |
| Clade: | Pseudosuchia |
| Clade: | Crocodylomorpha |
| Clade: | Crocodyliformes |
| Clade: | Metasuchia |
| Clade: | Neosuchia |
| Clade: | Eusuchia |
| Genus: | †Eosuchus Dollo, 1907 |
| Species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Eosuchus ("dawn crocodile") is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorph, traditionally regarded as a gavialoid crocodilian. It might have been among the most basal of all gavialoids, lying crownward of all other known members of the superfamily, including earlier putative members such as Thoracosaurus and Eothoracosaurus. Fossils have been found from France as well as eastern North America in Maryland, Virginia, and New Jersey. The strata from which specimens have been found date back to the late Paleocene and early Eocene epochs.
Discovery
[edit]
The name Eosuchus was first used in 1907 to describe a single specimen found from northern France near the Belgian border, assigned to the type species Eosuchus lerichei.[2]
A second species, Eosuchus minor, was actually discovered earlier in 1870 by Othniel Charles Marsh, but was assigned to the genus Gavialis. The Gavialis minor holotype specimen YPM 282 consisted of cranial fragments and isolated vertebrae found from the Manasquan Formation in Monmouth County, New Jersey, dating back to the Ypresian stage of the early Eocene. The species name minor refers to the relatively small estimated size of the animal, estimated at no more than 2 meters, when compared to other gavialoids such as the modern gharial, which can grow up to 5 meters in length. However, this species was later recognized as distinct from Gavialis on the basis of certain aspects of the known cranial material, in particular the large foramen aerum of the quadrate formed from the epithelial tube that connects the pneumatic chambers of the quadrate and articular. Another diagnostic feature thought to distinguish the species from Gavialis was the narrow interfenestral bar of the parietal bone that is relatively smooth and unsculptured when compared to other gavialoids such as Thoracosaurus. The new generic name Thecachampsoides was proposed for the species G. minor in 1986.[3] A close relationship between T. minor and Eosuchus lerichei was always evident, yet it was not until 2006 that the name Eosuchus was applied to the T. minor specimens, specifically on the basis of a fairly complete specimen called NJSM 15437 from the Vincentown Formation in New Jersey, of which there is a visibly exposed braincase which aids greatly in the taxonomic classification of the genus. The examination of specimens of Thecachampsoides minor with those of Eosuchus lerichei yielded many similarities between the two species, including the foramen aerum as well as other features such as a long nasal process between the premaxillae, dentary alveoli arranged in pairs, and a W-shaped basioccipital tuberosity. E. minor differs from E. lerichei on the basis of a noticeably wider nasal and prefrontals positioned anteriorly further up the skull than the lacrimals.[4]
Other material present from the Aquia Formation of Maryland and Virginia, which dates back to the early Paleocene, tends to be more complete. Some specimens found from these localities are known from nearly complete skulls that provide a more detailed view of the phylogenetic position of Eosuchus, and further aid in distinguishing E. minor from other gavialoids.
A Triassic rhynchosaur was originally named Eosuchus, although it is completely unrelated to the crocodyliform of the same name. The name of the rhynchosaur was later changed to Noteosuchus due to this preoccupation.[5]
Classification
[edit]
Eosuchus is often referred to as a "thoracosaur", a group that was constructed to include many basal forms of gavialoids that cannot be placed into any specific families of their own, yet do not form a true clade. The genus is distinct from gavialoids in still having a thin descending lamina positioned next to the pterygoid.
A phylogenetic analysis conducted in 1996 suggested that Eosuchus may be closely related to tomistomines such as the extant Tomistoma. There is further evidence of this relationship shown in the humeri of these crocodilians; both Eosuchus and tomistomines have a deeply concave deltopectoral crest, unlike the more triangular crests of Gavialis. A nasal-premaxilla contact and similar dentary and maxillary tooth counts also seem to suggest that there may be a close relationship between the genus and later tomistomines, although these features represent more primitive conditions that changed later in gavialoid history. Despite this, it is currently accepted that a close relationship between Eosuchus and tomistomines is not the case, and that the similarities between the two may just be superficial and that these characteristics are plesiomorphic to all gavialoids, being lost in more derived members such as the modern Gavialis.
Eosuchus lerichei and E. minor were included in the study on the phylogenetic relationships of putative fossil gavialoids published by Lee & Yates (2018). The authors considered it most likely that Eosuchus was not a gavialoid, or even a crocodylian, but rather a member of the clade of non-crocodylian eusuchians that also included the genera Argochampsa, Eogavialis, Eothoracosaurus and Thoracosaurus.[6]
Paleobiology
[edit]
The strata from which both species of Eosuchus have been found were thought to have formed in a marginal marine depositional environment, and thus probably reflect the actual environments that these animals would have inhabited. It has been proposed that early gavialoids were originally salt-tolerant coastal forms,[7] and the evidence seen in the case of Eosuchus is consistent with this theory. The internal surface of the prefrontal and lacrimal bones of E. lerichei are characterized by concave depressions, which in several marine lizards, iguanas and birds are where salt glands are housed, suggesting this species was capable of saltwater tolerance. [8] One specimen of E. minor from the Aquia Formation, USNM 299730, has a fossil oyster attached to the dorsal surface of the rostrum.
The fact that the two species of Eosuchus lived on either side of the Atlantic Ocean implies that these populations may have been separated geographically from one another while not necessarily having to be separated stratigraphically (that is, if the temporal ranges of the two species coincide with one another). More importantly, the separate biogeographic ranges of the two species may be evidence for a transoceanic dispersal event from one continent to the other. Since the presumed ages of the localities from which specimens have been found are quite similar yet inexact, it is currently unknown just what continent this dispersal event may have originated. A recent reevaluation of the holotype material of E. lerichei, which in the past has been poorly studied, suggests that it is the more basal species and thus would have been the ancestor of E. minor in Europe.[9]
References
[edit]- ^ Rio, Jonathan P.; Mannion, Philip D. (6 September 2021). "Phylogenetic analysis of a new morphological dataset elucidates the evolutionary history of Crocodylia and resolves the long-standing gharial problem". PeerJ. 9: e12094. doi:10.7717/peerj.12094. PMC 8428266. PMID 34567843.
- ^ Dollo, L. (1907). "Les reptiles de l'Éocène Inférieur de la Belgique et des régions voisines". Bulletin de la Société Belge de Géologie, de Paléontologie et d'Hydrologie. 21: 81–85.
- ^ Norell, M. A.; Storrs, G. W. (1986). "Catalogue and review of the type fossil crocodilians in the Yale Peabody Museum". Postula. 203: 1–28.
- ^ Brochu, C. A. (2006). "Osteology and phylogenetic significance of Eosuchus minor (Marsh, 1870) new combination, a longirostrine crocodylian from the Late Paleocene of North America". Journal of Paleontology. 80 (1): 162–186. doi:10.1666/0022-3360(2006)080[0162:OAPSOE]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 85578463.
- ^ Broom, Robert (1925). "On the South African rhynchocephaloid reptile "Eosuchus" colletti, Watson". Records of the Albany Museum. 3: 300–306.
- ^ Michael S. Y. Lee; Adam M. Yates (2018). "Tip-dating and homoplasy: reconciling the shallow molecular divergences of modern gharials with their long fossil record". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 285 (1881): 20181071. doi:10.1098/rspb.2018.1071. PMC 6030529. PMID 30051855.
- ^ Taplin, L. E.; Grigg, G. C. (1989). "Historical zoogeography of the eusuchian crocodilians: A physiological perspective". American Zoologist. 29 (3): 885–901. doi:10.1093/icb/29.3.885.
- ^ Burke, P. M. J.; Boerman, S. A; Perrichon, G; Martin, J. E.; Smith, T.; Vellekoop, J.; Mannion, P. D. (2024). "Endocranial anatomy and phylogenetic position of the crocodylian Eosuchus lerichei from the late Paleocene of northwestern Europe and potential adaptations for transoceanic dispersal in gavialoids". The Anatomical Record. doi:10.1002/ar.25569.
- ^ Delfino, M.; Pira, P.; Smith, T. (2005). "Anatomy and phylogeny of the gavialoid crocodylian Eosuchus lerichei from the Paleocene of Europe". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 50 (3): 565–580.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch

