Tétraphénylène — Wikipédia
| Tétraphénylène | |
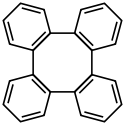 Structure du tétraphénylène. | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | tétrabenzo[a,c,e,g]cyclooctatétraène |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 2724868 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C24H16 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 304,383 8 ± 0,020 3 g/mol C 94,7 %, H 5,3 %, |
| Propriétés physiques | |
| T° fusion | 232 à 235 °C |
| Cristallographie | |
| Système cristallin | monoclinique[2] |
| Classe cristalline ou groupe d’espace | (no 15) |
| Paramètres de maille | a = 15,628 Å b = 13,126 Å |
| Volume | 1,23 g·cm-3 [2] |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
| modifier | |
Le tétraphénylène est un hydrocarbure aromatique polycyclique à quatre cycles, de formule C24H16.
Références
[modifier | modifier le code]- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) H. Irngartinger et W.R.K. Reibel, « Structures of dibenzo[a,e]cyclooctatetraene and tetrabenzo[a,c,e,g]cyclooctatetraene (o-tetraphenylene) », Acta Crystallographica Section B:Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry, vol. 37, , p. 1724-1728 (DOI 10.1107/S0567740881006985)


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch

