Ubenimex
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
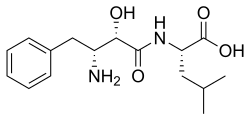
| IUPAC name N-[(2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutanoyl]-L-leucine | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (2S)-2-[(2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutanamido]-4-methylpentanoic acid | |
| Other names Bestatin; N-[(2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyryl]-L-leucine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.055.917 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H24N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 308.378 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 245 °C (473 °F; 518 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[2] | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Ubenimex (INN), also known more commonly as bestatin, is a competitive, reversible protease inhibitor. It is an inhibitor of arginyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase B),[3] leukotriene A4 hydrolase (a zinc metalloprotease that displays both epoxide hydrolase and aminopeptidase activities),[4] alanyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase M/N),[5] leucyl/cystinyl aminopeptidase (oxytocinase/vasopressinase),[6][7] and membrane dipeptidase (leukotriene D4 hydrolase). It is being studied for use in the treatment of acute myelocytic leukemia[8] and lymphedema.[9] It is derived from Streptomyces olivoreticuli.[10] Ubenimex has been found to inhibit the enzymatic degradation of oxytocin, vasopressin, enkephalins, and various other peptides and compounds.[citation needed]

See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ N-((2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyryl)-L-leucine at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ "Ubenimex". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- ^ Umezawa, H.; Aoyagi, T.; Suda, H.; Hamada, M.; Takeuchi, T. (1976). "Bestatin, an inhibitor of aminopeptidase B, produced by actinomycetes". The Journal of Antibiotics. 29 (29): 97–99. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.29.97. PMID 931798.
- ^ Muskardin, D.T.; Voelkel, N.F.; Fitzpatrick, F.A. (1994). "Modulation of pulmonary leukotriene formation and perfusion pressure by Bestatin, an inhibitor of leukotriene A4 hydrolase". Biochemical Pharmacology. 48 (48): 131–137. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(94)90232-1. PMID 8043014.
- ^ K Sekine; H Fujii; F Abe (1999). "Induction of apoptosis by Bestatin (ubenimex) in human leukemic cell lines". Leukemia. 13 (5): 729–734. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2401388. PMID 10374877.
- ^ Nakanishi Y, Nomura S, Okada M, Ito T, Katsumata Y, Kikkawa F, Hattori A, Tsujimoto M, Mizutani S (2000). "Immunoaffinity purification and characterization of native placental leucine aminopeptidase/oxytocinase from human placenta". Placenta. 21 (7): 628–34. doi:10.1053/plac.2000.0564. PMID 10985965.
- ^ Naruki M, Mizutani S, Goto K, Tsujimoto M, Nakazato H, Itakura A, Mizuno K, Kurauchi O, Kikkawa F, Tomoda Y (1996). "Oxytocin is hydrolyzed by an enzyme in human placenta that is identical to the oxytocinase of pregnancy serum". Peptides. 17 (2): 257–61. doi:10.1016/0196-9781(95)02124-8. PMID 8801531. S2CID 28486489.
- ^ Hirayama, Y; Sakamaki, S; Takayanagi, N; Tsuji, Y; Sagawa, T; Chiba, H; Matsunaga, T; Niitsu, Y (2003). "Chemotherapy with ubenimex corresponding to patient age and organ disorder for 18 cases of acute myelogeneous leukemia in elderly patients--effects, complications and long-term survival". Gan to Kagaku Ryoho. Cancer & Chemotherapy. 30 (8): 1113–8. PMID 12938265.
- ^ Tian, W; Rockson, S; Jiang, X; Kim, J; Begaye, A; Shuffle, EM; Tu, AB; Cribb, M; Nepiyushchikh, Z; Feroze, AH; Zamanian, RT; Dhillon, RT; Voelkel, NF; Peters-Golden, M; Kitajewski, J; Dixon, JB; Nicolls, MR (2017). "Leukotriene B4 antagonism ameliorates experimental lymphedema". Science Translational Medicine. 9 (389): eaal3920. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3920. PMID 28490670.
- ^ Bauvois, B; Dauzonne, D (January 2006). "Aminopeptidase-N/CD13 (EC 3.4.11.2) inhibitors: Chemistry, biological evaluations, and therapeutic prospects". Medicinal Research Reviews. 26 (1): 88–130. doi:10.1002/med.20044. PMC 7168514. PMID 16216010.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch